5-HT2C-like receptors in the brain of Xenopus laevis initiate sex-typical fictive vocalizations
- PMID: 19474172
- PMCID: PMC2724353
- DOI: 10.1152/jn.90469.2008
5-HT2C-like receptors in the brain of Xenopus laevis initiate sex-typical fictive vocalizations
Abstract
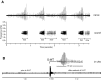
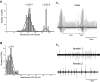
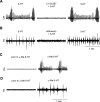
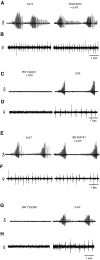
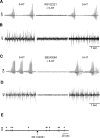
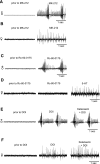
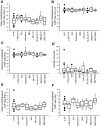
Vocalizations of male and female African clawed frogs (Xenopus laevis) are generated by brain stem central pattern generators. Serotonin (5-HT) is likely important for vocal initiation because, when applied in vitro, sex-typical fictive vocalizations are evoked from isolated brains. To explore the mechanisms underlying vocal initiation, we identified the types of serotonin receptors mediating vocal activation pharmacologically using a whole brain, fictive preparation. The results showed that 5-HT(2C)-like receptors are important for activation of fictive vocalizations in the sexes. 5-HT(2C) receptor agonists elicited fictive vocalizations, and 5-HT(2C) receptor antagonists blocked 5-HT-induced fictive vocalizations, whereas agonists and antagonists of 5-HT(2A) and 5-HT(2B) receptors failed to initiate or block 5-HT-induced fictive vocalizations in the sexes. The results indicate that serotonin initiates fictive vocalizations by binding to 5-HT(2C)-like receptors located either within or upstream of the vocal central pattern generator in both sexes. We conclude that the basic mechanism of vocal initiation is shared by the sexes despite the differences in the actual vocalizations between males and females. Sex-typical vocalizations, therefore, most likely arise from activation of different populations of 5-HT(2C) receptor expressing cells or from differential activation of downstream pattern generating neurons.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Rhythm generation, coordination, and initiation in the vocal pathways of male African clawed frogs.J Neurophysiol. 2017 Jan 1;117(1):178-194. doi: 10.1152/jn.00628.2016. Epub 2016 Oct 19. J Neurophysiol. 2017. PMID: 27760822 Free PMC article.
-
Endogenous serotonin acts on 5-HT2C-like receptors in key vocal areas of the brain stem to initiate vocalizations in Xenopus laevis.J Neurophysiol. 2010 Feb;103(2):648-58. doi: 10.1152/jn.00827.2009. Epub 2009 Dec 2. J Neurophysiol. 2010. PMID: 19955293 Free PMC article.
-
Pharmacological characterisation of the agonist radioligand binding site of 5-HT(2A), 5-HT(2B) and 5-HT(2C) receptors.Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 2004 Aug;370(2):114-23. doi: 10.1007/s00210-004-0951-4. Epub 2004 Jul 30. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 2004. PMID: 15322733
-
Prospects for serotonin 5-HT2R pharmacotherapy in psychostimulant abuse.Prog Brain Res. 2008;172:319-46. doi: 10.1016/S0079-6123(08)00916-3. Prog Brain Res. 2008. PMID: 18772040 Review.
-
Predictive in silico studies of human 5-hydroxytryptamine receptor subtype 2B (5-HT2B) and valvular heart disease.Curr Top Med Chem. 2013;13(11):1353-62. doi: 10.2174/15680266113139990039. Curr Top Med Chem. 2013. PMID: 23675941 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Rhythm generation, coordination, and initiation in the vocal pathways of male African clawed frogs.J Neurophysiol. 2017 Jan 1;117(1):178-194. doi: 10.1152/jn.00628.2016. Epub 2016 Oct 19. J Neurophysiol. 2017. PMID: 27760822 Free PMC article.
-
Frank Beach Award Winner: Steroids as neuromodulators of brain circuits and behavior.Horm Behav. 2014 Aug;66(3):552-60. doi: 10.1016/j.yhbeh.2014.07.014. Epub 2014 Aug 7. Horm Behav. 2014. PMID: 25110187 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The Xenopus amygdala mediates socially appropriate vocal communication signals.J Neurosci. 2013 Sep 4;33(36):14534-48. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.1190-13.2013. J Neurosci. 2013. PMID: 24005304 Free PMC article.
-
Endogenous serotonin acts on 5-HT2C-like receptors in key vocal areas of the brain stem to initiate vocalizations in Xenopus laevis.J Neurophysiol. 2010 Feb;103(2):648-58. doi: 10.1152/jn.00827.2009. Epub 2009 Dec 2. J Neurophysiol. 2010. PMID: 19955293 Free PMC article.
-
Context-dependent fluctuation of serotonin in the auditory midbrain: the influence of sex, reproductive state and experience.J Exp Biol. 2014 Feb 15;217(Pt 4):526-35. doi: 10.1242/jeb.087627. Epub 2013 Nov 6. J Exp Biol. 2014. PMID: 24198252 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Bancila M, Verge D, Rampin O, Backstrom JR, Sanders-Bush E, McKenna KE, Marson L, Calas A, Giuliano F. 5-Hydroxytryptamine2C receptors on spinal neurons controlling penile erection in the rat. Neuroscience 92: 1523–1537, 1999. - PubMed
-
- Barnes NM, Sharp T. A review of central 5-HT receptors and their function. Neuropharmacology 38: 1083–1152, 1999. - PubMed
-
- Baxter G, Kennett G, Blaney F, Blackburn T. 5-HT2 receptor subtypes: a family re-united? Trends Pharmacol Sci 16: 105–110, 1995. - PubMed
-
- Bishop C, Tessamer JL, Ullrich T, Rice KC, Walker PD. Serotonin 5-HT2A receptors underlie increased motor behaviors induced in dopamine-depleted rats by intrastriatal 5-HT2A/2C agonism. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 310: 687–694, 2004. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

