The full-length calcium-sensing receptor dampens the calcemic response to 1alpha,25(OH)2 vitamin D3 in vivo independently of parathyroid hormone
- PMID: 19474191
- PMCID: PMC2739709
- DOI: 10.1152/ajprenal.00164.2009
The full-length calcium-sensing receptor dampens the calcemic response to 1alpha,25(OH)2 vitamin D3 in vivo independently of parathyroid hormone
Abstract
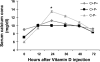
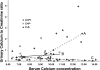
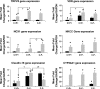
1Alpha,25(OH)(2) vitamin D(3) [1,25(OH)(2)D(3)] increases serum Ca(2+) concentration in vivo, an action counteracted by activation of the Ca(2+)-sensing receptor (CaSR), which decreases parathyroid hormone (PTH) secretion and increases renal Ca(2+) excretion. Relatively little is known of the role the CaSR plays in this response through its potentially direct actions in kidney, gut, and bone independently of PTH. We report PTH-independent roles of the CaSR in modulating the response to exogenous 1,25(OH)(2)D(3) in mice with targeted disruption of both the CaSR and PTH genes (C(-)P(-)) compared with that in mice with disruption of the PTH gene alone (C(+)P(-)) or wild-type mice (C(+)P(+)). After intraperitoneal injection of 0.5 ng/g body wt 1,25(OH)(2)D(3), peak calcemic responses were observed at 24 h in all three genotypes in association with 1) a greater increase in serum Ca(2+) in C(-)P(-) mice than in the other genotypes on a Ca(2+)-replete diet that was attenuated by a Ca(2+)-deficient diet and pamidronate, 2) increased urinary Ca(2+)-to-creatinine ratios (UCa/Cr) in the C(+)P(-) and C(+)P(+) mice but a lowered ratio in the C(-)P(-) mice on a Ca(2+)-replete diet, and 3) no increase in calcitonin (CT) secretion in the C(+)P(+) and C(+)P(-) mice and a small increase in the C(-)P(-) mice. PTH deficiency had the anticipated effects on the expression of key genes involved in Ca(2+) transport at baseline in the duodenum and kidney, and injection of 1,25(OH)(2)D(3) increased gene expression 8 h later. However, the changes in the genes evaluated did not fully explain the differences in serum Ca(2+) seen among the genotypes. In conclusion, mice lacking the full-length CaSR have increased sensitivity to the calcemic action of 1,25(OH)(2)D(3) in the setting of PTH deficiency. This is principally from enhanced 1,25(OH)(2)D(3)-mediated gut Ca(2+) absorption and decreased renal Ca(2+) excretion, without any differences in bone-related release of Ca(2+) or CT secretion among the three genotypes that could explain the differences in their calcemic responses.
Figures
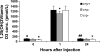





References
-
- Dusso A, Brown A, Slatoposky E. Vitamin D. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol 289: F8–F28, 2005. - PubMed
-
- Ba J, Friedman PA. Calcium-sensing receptor regulation of renal mineral ion transport. Cell Calcium 35: 229–237, 2004. - PubMed
-
- Brown EM Calcium sensing by endocrine cells. Endocr Pathol 15: 187–220, 2004. - PubMed
-
- Buchan AM, Squires PE, Ring M, Meloche RM. Mechanism of action of the calcium-sensing receptor in human antral gastrin cells. Gastroenterology 120: 1128–1139, 2001. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

