Mitotic epitopes are incorporated into age-dependent neurofibrillary tangles in Niemann-Pick disease type C
- PMID: 19476463
- PMCID: PMC8094688
- DOI: 10.1111/j.1750-3639.2009.00286.x
Mitotic epitopes are incorporated into age-dependent neurofibrillary tangles in Niemann-Pick disease type C
Abstract
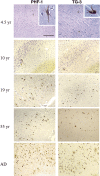
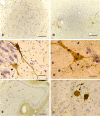
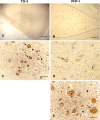
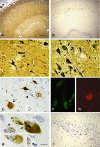
The mechanism underlying neurofibrillary tangles (NFTs) in Alzheimer's disease (AD) and other neurodegenerative disorders remains elusive. Niemann-Pick disease type C (NPC) is a kind of genetic neurovisceral disorder in which the intracellular sequestration of cholesterol and other lipids in neurons, NFT formation and neuronal degeneration in brain are the neuropathology hallmarks. The age of onset and progression of the disease vary dramatically. We have analyzed the hippocampus from 17 NPC cases, aged from 7 months to 55 years, to depict the temporal characteristics of NFT formation. Unexpectedly, classic NFT was observed in about 4-year-old NPC brain, suggesting that NFT is not aging dependent, and that juvenile brain neurons satisfy the requirements for NFT formation. NFT in the hippocampus of NPC was significantly increased in number with the advance of age. More importantly, multiple mitotic phase markers, which are not usually found in normal mature neurons, were abundant in the affected neurons and incorporated into NFT. The unusual activation of cdc2/cyclin B kinase and downstream mitotic indices are closely associated with the age-dependent NFT formation, signifying the contribution of abortive cell cycle to neurodegeneration. The cdc2 inhibitors may be therapeutically used for early intervention of neurodegeneration and NFT formation in NPC.
Figures
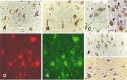
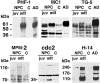
Similar articles
-
Aberrant expression of mitotic cdc2/cyclin B1 kinase in degenerating neurons of Alzheimer's disease brain.J Neurosci. 1997 May 15;17(10):3588-98. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.17-10-03588.1997. J Neurosci. 1997. PMID: 9133382 Free PMC article.
-
Niemann-Pick disease type C yields possible clue for why cerebellar neurons do not form neurofibrillary tangles.Neurobiol Dis. 2002 Nov;11(2):285-97. doi: 10.1006/nbdi.2002.0551. Neurobiol Dis. 2002. PMID: 12505421
-
Constitutive Cdc25B tyrosine phosphatase activity in adult brain neurons with M phase-type alterations in Alzheimer's disease.Neuroscience. 2001;105(3):639-50. doi: 10.1016/s0306-4522(01)00219-6. Neuroscience. 2001. PMID: 11516829
-
Cellular mechanism of U18666A-mediated apoptosis in cultured murine cortical neurons: bridging Niemann-Pick disease type C and Alzheimer's disease.Cell Signal. 2006 Nov;18(11):1844-53. doi: 10.1016/j.cellsig.2006.04.006. Epub 2006 May 7. Cell Signal. 2006. PMID: 16797161 Review.
-
Neurofibrillary changes undergoing morphological and biochemical changes - How does tau with the profile shift of from four repeat to three repeat spread in Alzheimer brain?Neuropathology. 2020 Oct;40(5):450-459. doi: 10.1111/neup.12669. Epub 2020 Jul 22. Neuropathology. 2020. PMID: 32698244 Review.
Cited by
-
Differential involvement of hippocampal subfields in Niemann-Pick type C disease: a case-control study.Metab Brain Dis. 2021 Oct;36(7):2071-2078. doi: 10.1007/s11011-021-00782-9. Epub 2021 Jun 19. Metab Brain Dis. 2021. PMID: 34146215
-
Mitotic spindle defects and chromosome mis-segregation induced by LDL/cholesterol-implications for Niemann-Pick C1, Alzheimer's disease, and atherosclerosis.PLoS One. 2013 Apr 12;8(4):e60718. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0060718. Print 2013. PLoS One. 2013. PMID: 23593294 Free PMC article.
-
Lysosomal dysfunction in a mouse model of Sandhoff disease leads to accumulation of ganglioside-bound amyloid-β peptide.J Neurosci. 2012 Apr 11;32(15):5223-36. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.4860-11.2012. J Neurosci. 2012. PMID: 22496568 Free PMC article.
-
Imaging of tau deposits in adults with Niemann-Pick type C disease: a case-control study.Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imaging. 2019 May;46(5):1132-1138. doi: 10.1007/s00259-019-4273-7. Epub 2019 Jan 28. Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imaging. 2019. PMID: 30690666
-
Distinct Rab7-related Endosomal-Autophagic-Lysosomal Dysregulation Observed in Cortex and Hippocampus in APPswe/PSEN1dE9 Mouse Model of Alzheimer's Disease.Chin Med J (Engl). 2017 Dec 20;130(24):2941-2950. doi: 10.4103/0366-6999.220311. Chin Med J (Engl). 2017. PMID: 29237927 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Auer IA, Schmidt ML, Lee VM, Curry B, Suzuki K, Shin RW et al (1995) Paired helical filament tau (PHFtau) in Niemann–Pick type C disease is similar to PHFtau in Alzheimer's disease. Acta Neuropathol 90:547–551. - PubMed
-
- Braak E, Braak H, Mandelkow EM (1994) A sequence of cytoskeleton changes related to the formation of neurofibrillary tangles and neuropil threads. Acta Neuropathol 87:554–567. - PubMed
-
- Braak H, Braak E (1991) Neuropathological stageing of Alzheimer‐related changes. Acta Neuropathol 82:239–259. - PubMed
-
- Braak H, Braak E (1997) Frequency of stages of Alzheimer‐related lesions in different age categories. Neurobiol Aging 18:351–357. - PubMed
-
- Braak H, Braak E, Bohl J (1993) Staging of Alzheimer‐related cortical destruction. Eur Neurol 33:403–408. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

