Following TRAIL's path in the immune system
- PMID: 19476510
- PMCID: PMC2691779
- DOI: 10.1111/j.1365-2567.2009.03058.x
Following TRAIL's path in the immune system
Abstract
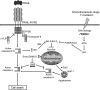
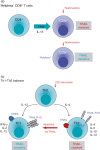
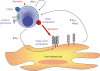
The members of the tumour necrosis factor (TNF) superfamily of cytokines play important roles in the regulation of various immune-cell functions. Likewise, induction of cell death by apoptosis is indispensable for the normal functioning of the immune system. There are two major pathways of apoptosis induction. The intrinsic, or mitochondrial, pathway is regulated by the activation and interaction of members of the Bcl-2 family. The extrinsic, or death receptor, pathway is triggered by certain TNF family members when they engage their respective cognate receptors on the surface of the target cell. Hence, cell-to-cell-mediated death signals are induced by activation of these death receptor-ligand systems. Besides TNF itself and the CD95 (Fas/APO-1) ligand (FasL/Apo1L), the TNF-related apoptosis-inducing ligand (TRAIL/Apo2L) belongs to the subfamily of ligands that is responsible for extrinsic induction of cell death. Depending on their status of stimulation, TRAIL can be expressed by various cells of the immune system, amongst them natural killer (NK) cells, T cells, natural killer T cells (NKT cells), dendritic cells and macrophages. TRAIL has been implicated in immunosuppressive, immunoregulatory and immune-effector functions. With respect to pathological challenges, TRAIL and its receptors have been shown to play important roles in the immune response to viral infections and in immune surveillance of tumours and metastases. In this review we summarize the current knowledge on the role of TRAIL and its receptors in the immune system and, based on this, we discuss future directions of research into the diverse functions of this fascinating receptor-ligand system.
Figures
References
-
- Opferman JT, Korsmeyer SJ. Apoptosis in the development and maintenance of the immune system. Nat Immunol. 2003;4:410–5. - PubMed
-
- Lunemann JD, Waiczies S, Ehrlich S, Wendling U, Seeger B, Kamradt T, Zipp F. Death ligand TRAIL induces no apoptosis but inhibits activation of human (auto)antigen-specific T cells. J Immunol. 2002;168:4881–8. - PubMed
-
- Walczak H, Haas TL. Biochemical analysis of the native TRAIL death-inducing signaling complex. Methods Mol Biol. 2008;414:221–39. - PubMed
-
- Waterhouse NJ, Ricci JE, Green DR. And all of a sudden it's over: mitochondrial outer-membrane permeabilization in apoptosis. Biochimie. 2002;3:113–21. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

