DNA-like class R inhibitory oligonucleotides (INH-ODNs) preferentially block autoantigen-induced B-cell and dendritic cell activation in vitro and autoantibody production in lupus-prone MRL-Fas(lpr/lpr) mice in vivo
- PMID: 19476613
- PMCID: PMC2714127
- DOI: 10.1186/ar2710
DNA-like class R inhibitory oligonucleotides (INH-ODNs) preferentially block autoantigen-induced B-cell and dendritic cell activation in vitro and autoantibody production in lupus-prone MRL-Fas(lpr/lpr) mice in vivo
Abstract
Introduction: B cells have many different roles in systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE), ranging from autoantigen recognition and processing to effector functions (for example, autoantibody and cytokine secretion). Recent studies have shown that intracellular nucleic acid-sensing receptors, Toll-like receptor (TLR) 7 and TLR9, play an important role in the pathogenesis of SLE. Dual engagement of rheumatoid factor-specific AM14 B cells through the B-cell receptor (BCR) and TLR7/9 results in marked proliferation of autoimmune B cells. Thus, strategies to preferentially block innate activation through TLRs in autoimmune B cells may be preferred over non-selective B-cell depletion.
Methods: We have developed a new generation of DNA-like compounds named class R inhibitory oligonucleotides (INH-ODNs). We tested their effectiveness in autoimmune B cells and interferon-alpha-producing dendritic cells in vitro and in lupus-prone MRL-Faslpr/lpr mice in vivo.
Results: Class R INH-ODNs have 10- to 30-fold higher inhibitory potency when autoreactive B cells are synergistically activated through the BCR and associated TLR7 or 9 than when stimulation occurs via non-BCR-engaged TLR7/9. Inhibition of TLR9 requires the presence of both CCT and GGG triplets in an INH-ODN, whereas the inhibition of the TLR7 pathway appears to be sequence-independent but dependent on the phosphorothioate backbone. This difference was also observed in the MRL-Faslpr/lpr mice in vivo, where the prototypic class R INH-ODN was more effective in curtailing abnormal autoantibody secretion and prolonging survival.
Conclusions: The increased potency of class R INH-ODNs for autoreactive B cells and dendritic cells may be beneficial for lupus patients by providing pathway-specific inhibition yet allowing them to generate protective immune response when needed.
Figures
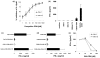
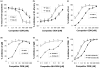
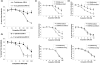
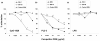

Comment in
-
Inhibitory short synthetic oligodeoxynucleotides and lupus.Arthritis Res Ther. 2009;11(3):116. doi: 10.1186/ar2726. Epub 2009 Jun 26. Arthritis Res Ther. 2009. PMID: 19591639 Free PMC article.
Similar articles
-
Guanine modification of inhibitory oligonucleotides potentiates their suppressive function.J Immunol. 2013 Sep 15;191(6):3240-53. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.1300706. Epub 2013 Aug 21. J Immunol. 2013. PMID: 23966630
-
Guanine-modified inhibitory oligonucleotides efficiently impair TLR7- and TLR9-mediated immune responses of human immune cells.PLoS One. 2015 Feb 19;10(2):e0116703. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0116703. eCollection 2015. PLoS One. 2015. PMID: 25695778 Free PMC article.
-
Engagement of the B cell receptor for antigen differentially affects B cell responses to Toll-like receptor-7 agonists and antagonists in BXSB mice.Clin Exp Immunol. 2011 Mar;163(3):392-403. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2249.2010.04307.x. Epub 2011 Jan 14. Clin Exp Immunol. 2011. PMID: 21235537 Free PMC article.
-
Targeting Toll-like receptor signaling in plasmacytoid dendritic cells and autoreactive B cells as a therapy for lupus.Arthritis Res Ther. 2006;8(1):203. doi: 10.1186/ar1888. Epub 2006 Jan 10. Arthritis Res Ther. 2006. PMID: 16542467 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The central and multiple roles of B cells in lupus pathogenesis.Immunol Rev. 1999 Jun;169:107-21. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-065x.1999.tb01310.x. Immunol Rev. 1999. PMID: 10450512 Review.
Cited by
-
Role of nucleic acid sensing in the pathogenesis of type 1 diabetes.World J Diabetes. 2021 Oct 15;12(10):1655-1673. doi: 10.4239/wjd.v12.i10.1655. World J Diabetes. 2021. PMID: 34754369 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Nucleic acid sensing receptors in systemic lupus erythematosus: development of novel DNA- and/or RNA-like analogues for treating lupus.Clin Exp Immunol. 2010 Aug;161(2):208-22. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2249.2010.04176.x. Epub 2010 May 7. Clin Exp Immunol. 2010. PMID: 20456414 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Aggregation and secondary loop structure of oligonucleotides do not determine their ability to inhibit TLR9.Int Immunopharmacol. 2011 Aug;11(8):1032-7. doi: 10.1016/j.intimp.2011.02.023. Epub 2011 Mar 2. Int Immunopharmacol. 2011. PMID: 21376154 Free PMC article.
-
Immunomodulatory spherical nucleic acids.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2015 Mar 31;112(13):3892-7. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1502850112. Epub 2015 Mar 16. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2015. PMID: 25775582 Free PMC article.
-
The potential importance of Toll-like receptors in ankylosing spondylitis.Int J Clin Rheumtol. 2011;6(6):649-654. doi: 10.2217/IJR.11.61. Int J Clin Rheumtol. 2011. PMID: 22389660 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

