Genotyping and expression analysis of IDO2 in human pancreatic cancer: a novel, active target
- PMID: 19476837
- PMCID: PMC3176891
- DOI: 10.1016/j.jamcollsurg.2008.12.018
Genotyping and expression analysis of IDO2 in human pancreatic cancer: a novel, active target
Abstract
Background: The recently discovered indoleamine 2,3-dioxygenase-2 (IDO2) gene has 2 functional polymorphisms that abolish its enzymatic activity. We hypothesize that expression of the IDO2 enzyme in primary pancreatic ductal adenocarcinomas (PDA) can help cancer cells evade immune detection.
Study design: Because the IDO2 enzyme might be the preferential target of d-1-methyl-tryptophan, a clinical lead inhibitor of IDO currently being evaluated in phase I trials, we sequenced IDO2 in 36 pancreatic specimens and evaluated its expression.
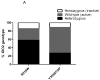
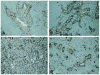
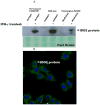
Results: We found that 58% (21 of 36) of cases were heterozygous for the R248W polymorphism; 28% (10 of 36) were homozygous wild-type; and only 14% (5 of 36) were homozygous for the functionally inactive polymorphism. As for the Y359STOP polymorphism, we found that 27% (10 of 36) of cases were heterozygous, 62% (22 of 36) were homozygous wild-type, and only 11% (4 of 36) were homozygous for this functionally inactive allele. Ruling out the possibility of compound polymorphic variants, we estimated 75% of our resected patient cohort had an active IDO2 enzyme, with a conservative estimate that 58% of the patients had at least 1 functional allele. IDO2 was expressed in PDA tissue from each genetically polymorphic subgroup. We also detected IDO2 protein expression in the genetically distinct pancreatic cancer cell lines after exposure with interferon-gamma.
Conclusions: This is the first study to report IDO2 expression in PDA and related cancers indicating that IDO2 genetic polymorphisms do not negate interferon-gamma-inducible protein expression. Taken together, our data strongly suggest that the clinical lead compound d-1-methyl-tryptophan might be useful in treatment of PDA.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Indoleamine 2,3-dioxygenase 2 depletion suppresses tumor growth in a mouse model of Lewis lung carcinoma.Cancer Sci. 2019 Oct;110(10):3061-3067. doi: 10.1111/cas.14179. Epub 2019 Sep 25. Cancer Sci. 2019. PMID: 31444833 Free PMC article.
-
A Sub-Type of Familial Pancreatic Cancer: Evidence and Implications of Loss-of-Function Polymorphisms in Indoleamine-2,3-Dioxygenase-2.J Am Coll Surg. 2018 Apr;226(4):596-603. doi: 10.1016/j.jamcollsurg.2017.12.052. Epub 2018 Feb 7. J Am Coll Surg. 2018. PMID: 29426021 Free PMC article.
-
IDO1 and IDO2 are expressed in human tumors: levo- but not dextro-1-methyl tryptophan inhibits tryptophan catabolism.Cancer Immunol Immunother. 2009 Jan;58(1):153-7. doi: 10.1007/s00262-008-0513-6. Epub 2008 Apr 17. Cancer Immunol Immunother. 2009. PMID: 18418598 Free PMC article.
-
The Two Sides of Indoleamine 2,3-Dioxygenase 2 (IDO2).Cells. 2024 Nov 16;13(22):1894. doi: 10.3390/cells13221894. Cells. 2024. PMID: 39594642 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Indoleamine 2,3-dioxygenase-2; a new enzyme in the kynurenine pathway.Int J Biochem Cell Biol. 2009 Mar;41(3):467-71. doi: 10.1016/j.biocel.2008.01.005. Epub 2008 Jan 11. Int J Biochem Cell Biol. 2009. PMID: 18282734 Review.
Cited by
-
Diaryl hydroxylamines as pan or dual inhibitors of indoleamine 2,3-dioxygenase-1, indoleamine 2,3-dioxygenase-2 and tryptophan dioxygenase.Eur J Med Chem. 2019 Jan 15;162:455-464. doi: 10.1016/j.ejmech.2018.11.010. Epub 2018 Nov 14. Eur J Med Chem. 2019. PMID: 30469041 Free PMC article.
-
Indoleamine 2,3-dioxygenase 2 depletion suppresses tumor growth in a mouse model of Lewis lung carcinoma.Cancer Sci. 2019 Oct;110(10):3061-3067. doi: 10.1111/cas.14179. Epub 2019 Sep 25. Cancer Sci. 2019. PMID: 31444833 Free PMC article.
-
Tryptophan and Its Metabolites in Lung Cancer: Basic Functions and Clinical Significance.Front Oncol. 2021 Aug 6;11:707277. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2021.707277. eCollection 2021. Front Oncol. 2021. PMID: 34422661 Free PMC article. Review.
-
IDO1 and IDO2 non-synonymous gene variants: correlation with crohn's disease risk and clinical phenotype.PLoS One. 2014 Dec 26;9(12):e115848. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0115848. eCollection 2014. PLoS One. 2014. PMID: 25541686 Free PMC article.
-
IDO inhibits a tryptophan sufficiency signal that stimulates mTOR: A novel IDO effector pathway targeted by D-1-methyl-tryptophan.Oncoimmunology. 2012 Dec 1;1(9):1460-1468. doi: 10.4161/onci.21716. Oncoimmunology. 2012. PMID: 23264892 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Kennedy EP, Yeo CJ. The case for routine use of adjuvant therapy in pancreatic cancer. J Surg Oncol. 2007;95:597–603. - PubMed
-
- Winter JM, Cameron JL, Campbell KA, et al. 1423 pancreaticoduodenectomies for pancreatic cancer: A single-institution experience. J Gastrointest Surg. 2006;10:1199–210. discussion 210-1. - PubMed
-
- Zitvogel L, Tesniere A, Kroemer G. Cancer despite immunosurveillance: immunoselection and immunosubversion. Nat Rev Immunol. 2006;6:715–27. - PubMed
-
- Witkiewicz A, Williams TK, Cozzitorto J, et al. Expression of indoleamine 2,3-dioxygenase in metastatic pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma recruits regulatory T cells to avoid immune detection. J Am Coll Surg. 2008;206:849–54. discussion 54-6. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

