Surgical management of solid-pseudopapillary neoplasms of the pancreas (Franz or Hamoudi tumors): a large single-institutional series
- PMID: 19476869
- PMCID: PMC3109868
- DOI: 10.1016/j.jamcollsurg.2009.01.044
Surgical management of solid-pseudopapillary neoplasms of the pancreas (Franz or Hamoudi tumors): a large single-institutional series
Abstract
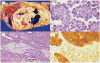
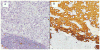
Background: Solid-pseudopapillary neoplasms (SPNs) are rare pancreatic tumors with malignant potential. Clinicopathologic characteristics and outcomes of patients with SPN were reviewed.
Study design: Longterm outcomes were evaluated in patients with an SPN who were followed from 1970 to 2008.
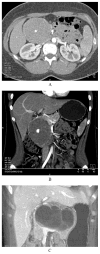
Results: Thirty-seven patients were identified with an SPN. Thirty-three (89%) were women, and median age at diagnosis was 32 years. Most patients were symptomatic; the most common symptom was abdominal pain (81%). Thirty-six patients underwent resection; one patient with distant metastases was not operated on. There were no 30-day mortalities. Median tumor size was 4.5 cm. Thirty-four patients underwent an R0 resection, 1 had an R1 resection, and 1 had an R2 resection. Two patients had lymph node metastases, and one patient had perineural invasion. After resection, 34 (94%) patients remain alive. One patient died of unknown causes 9.4 years after resection, and another died of unrelated causes 25.6 years after operation. The patient with widespread disease who didn't have resection died 11 months after diagnosis. Thirty-five of the 36 patients having resection remained disease free, including those who died of unrelated causes (median followup, 4.8 years). One patient developed a recurrence 7.7 years after complete resection. She was treated with gemcitabine and remains alive 13.6 months after recurrence.
Conclusions: SPNs are rare neoplasms with malignant potential found primarily in young women. Formal surgical resection may be performed safely and is associated with longterm survival.
Figures
References
-
- Martin RC, Klimstra DS, Brennan MF, Conlon KC. Solid-pseudopapillary tumor of the pancreas: a surgical enigma? Ann Surg Oncol. 2002;9:35–40. - PubMed
-
- Ng KH, Tan PH, Thng CH, Ooi LL. Solid pseudopapillary tumour of the pancreas. A N Z J Surg. 2003;73:410–415. - PubMed
-
- Papavramidis T, Papavramidis S. Solid pseudopapillary tumors of the pancreas: review of 718 patients reported in English literature. J Am Coll Surg. 2005;200:965–972. - PubMed
-
- Frantz VK. Atlas of tumor pathology. Washington, DC: US Armed Forces Institute of Pathology; 1959. Tumors of the pancreas; pp. 32–33.
-
- Hamoudi AB, Misugi K, Grosfeld JL, Reiner CB. Papillary epithelial neoplasm of pancreas in a child. Report of a case with electron microscopy. Cancer. 1970;26:1126–1134. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

