Functional and evolutionary insights into human brain development through global transcriptome analysis
- PMID: 19477152
- PMCID: PMC2739738
- DOI: 10.1016/j.neuron.2009.03.027
Functional and evolutionary insights into human brain development through global transcriptome analysis
Abstract
Our understanding of the evolution, formation, and pathological disruption of human brain circuits is impeded by a lack of comprehensive data on the developing brain transcriptome. A whole-genome, exon-level expression analysis of 13 regions from left and right sides of the mid-fetal human brain revealed that 76% of genes are expressed, and 44% of these are differentially regulated. These data reveal a large number of specific gene expression and alternative splicing patterns, as well as coexpression networks, associated with distinct regions and neurodevelopmental processes. Of particular relevance to cognitive specializations, we have characterized the transcriptional landscapes of prefrontal cortex and perisylvian speech and language areas, which exhibit a population-level global expression symmetry. We show that differentially expressed genes are more frequently associated with human-specific evolution of putative cis-regulatory elements. These data provide a wealth of biological insights into the complex transcriptional and molecular underpinnings of human brain development and evolution.
Figures

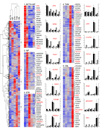
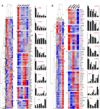
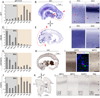
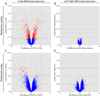
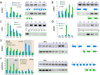
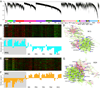
Comment in
-
Transcriptional regulation and alternative splicing make for better brains.Neuron. 2009 May 28;62(4):455-7. doi: 10.1016/j.neuron.2009.05.006. Neuron. 2009. PMID: 19477147
References
-
- Andrews W, Liapi A, Plachez C, Camurri L, Zhang J, Mori S, Murakami F, Parnavelas JG, Sundaresan V, Richards LJ. Robo1 regulates the development of major axon tracts and interneuron migration in the forebrain. Development. 2006;133:2243–2252. - PubMed
-
- Aruga J. The role of Zic genes in neural development. Mol. Cell Neurosci. 2004;26:205–221. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

