Separate neural mechanisms underlie choices and strategic preferences in risky decision making
- PMID: 19477159
- PMCID: PMC3213208
- DOI: 10.1016/j.neuron.2009.04.007
Separate neural mechanisms underlie choices and strategic preferences in risky decision making
Abstract
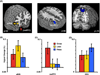
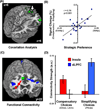
Adaptive decision making in real-world contexts often relies on strategic simplifications of decision problems. Yet, the neural mechanisms that shape these strategies and their implementation remain largely unknown. Using an economic decision-making task, we dissociate brain regions that predict specific choices from those predicting an individual's preferred strategy. Choices that maximized gains or minimized losses were predicted by functional magnetic resonance imaging activation in ventromedial prefrontal cortex or anterior insula, respectively. However, choices that followed a simplifying strategy (i.e., attending to overall probability of winning) were associated with activation in parietal and lateral prefrontal cortices. Dorsomedial prefrontal cortex, through differential functional connectivity with parietal and insular cortex, predicted individual variability in strategic preferences. Finally, we demonstrate that robust decision strategies follow from neural sensitivity to rewards. We conclude that decision making reflects more than compensatory interaction of choice-related regions; in addition, specific brain systems potentiate choices depending on strategies, traits, and context.
Figures

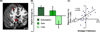
References
-
- Barraclough DJ, Conroy ML, Lee D. Prefrontal cortex and decision making in a mixed-strategy game. Nat Neurosci. 2004;7:404–410. - PubMed
-
- Bechara A, Tranel D, Damasio H. Characterization of the decision-making deficit of patients with ventromedial prefrontal cortex lesions. Brain. 2000;123:2189–2202. - PubMed
-
- Behrens TE, Woolrich MW, Walton ME, Rushworth MF. Learning the value of information in an uncertain world. Nat Neurosci. 2007;10:1214–1221. - PubMed
-
- Birnbaum MH. New paradoxes of risky decision making. Psychological Review. 2008;115:463–501. - PubMed
-
- Botvinick M, Nystrom LE, Fissell K, Carter CS, Cohen JD. Conflict monitoring versus selection-for-action in anterior cingulate cortex. Nature. 1999;402:179–181. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

