Structural and functional modules in RNA interference
- PMID: 19477631
- PMCID: PMC2721689
- DOI: 10.1016/j.sbi.2009.04.006
Structural and functional modules in RNA interference
Abstract
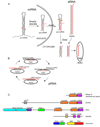
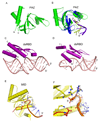
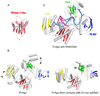
RNA interference (RNAi) uses small RNA molecules to regulate transcriptional and post-transcriptional gene expression. In recent years, a number of structural studies provided insights into the molecular architecture and mechanism of functional modules of RNAi. Mechanisms of nucleic acid recognition and cleavage have been revealed by structural studies of proteins and their nucleic acid complexes involved in RNA biogenesis, for example, Argonaute, PIWI, RNase III, Dicer, Drosha, and DGCR8. While quite a few questions remain, an excellent structural and mechanistic overview of RNAi processes has already emerged. In this review, we examine functional modules and their assemblies in RNAi processes.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Binding and cleavage specificities of human Argonaute2.J Biol Chem. 2009 Sep 18;284(38):26017-28. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M109.010835. Epub 2009 Jul 22. J Biol Chem. 2009. PMID: 19625255 Free PMC article.
-
Molecular dynamics simulation in RNA interference.Curr Med Chem. 2014 Jun;21(17):1968-75. doi: 10.2174/0929867321666131218100234. Curr Med Chem. 2014. PMID: 24350843 Review.
-
An unusual Dicer-like1 protein fuels the RNA interference pathway in Trypanosoma brucei.RNA. 2006 Dec;12(12):2063-72. doi: 10.1261/rna.246906. Epub 2006 Oct 19. RNA. 2006. PMID: 17053086 Free PMC article.
-
Characterization of the interactions between mammalian PAZ PIWI domain proteins and Dicer.EMBO Rep. 2004 Feb;5(2):189-94. doi: 10.1038/sj.embor.7400070. Epub 2004 Jan 16. EMBO Rep. 2004. PMID: 14749716 Free PMC article.
-
Dicer-independent processing of small RNA duplexes: mechanistic insights and applications.Nucleic Acids Res. 2017 Oct 13;45(18):10369-10379. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkx779. Nucleic Acids Res. 2017. PMID: 28977573 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
A simple Bayesian estimate of direct RNAi gene regulation events from differential gene expression profiles.BMC Genomics. 2011 May 20;12:250. doi: 10.1186/1471-2164-12-250. BMC Genomics. 2011. PMID: 21599879 Free PMC article.
-
Germ-line deletion in DICER1 revealed by a novel MLPA assay using synthetic oligonucleotides.Eur J Hum Genet. 2014 Apr;22(4):564-7. doi: 10.1038/ejhg.2013.215. Epub 2013 Sep 25. Eur J Hum Genet. 2014. PMID: 24065110 Free PMC article.
-
Novel endoribonucleases as central players in various pathways of eukaryotic RNA metabolism.RNA. 2010 Sep;16(9):1692-724. doi: 10.1261/rna.2237610. Epub 2010 Jul 30. RNA. 2010. PMID: 20675404 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Development of RNA Interference Trigger-Mediated Gene Silencing in Entamoeba invadens.Infect Immun. 2016 Mar 24;84(4):964-975. doi: 10.1128/IAI.01161-15. Print 2016 Apr. Infect Immun. 2016. PMID: 26787723 Free PMC article.
-
Nucleases: diversity of structure, function and mechanism.Q Rev Biophys. 2011 Feb;44(1):1-93. doi: 10.1017/S0033583510000181. Epub 2010 Sep 21. Q Rev Biophys. 2011. PMID: 20854710 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Bushati N, Cohen SM. microRNA functions. Annu Rev Cell Dev Biol. 2007;23:175–205. - PubMed
-
- Filipowicz W, Bhattacharyya SN, sonenberg N. Mechanisms of posttranscriptional regulation by microRNAs: are the answers in sight? Nat Rev Genet. 2008;9:102–114. - PubMed
-
- Rana TM. Illuminating the silence: understanding the structure and function of small RNAs. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2007;8:23–36. - PubMed
-
- Chapman EJ, Carrington JC. Specialization and evolution of endogenous small RNA pathways. Nat Rev Genet. 2007;8:884–896. - PubMed
-
- Zamore PD, Haley B. the big world of small RNAs. Science. 2005;309:1519–1524. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

