Compartmentalizing VEGF-induced ERK2/1 signaling in placental artery endothelial cell caveolae: a paradoxical role of caveolin-1 in placental angiogenesis in vitro
- PMID: 19477952
- PMCID: PMC2737550
- DOI: 10.1210/me.2008-0475
Compartmentalizing VEGF-induced ERK2/1 signaling in placental artery endothelial cell caveolae: a paradoxical role of caveolin-1 in placental angiogenesis in vitro
Abstract
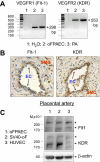
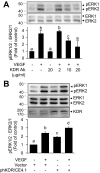
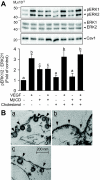
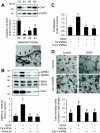
On vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) stimulation, both VEGF R1 and R2 receptors were phosphorylated in ovine fetoplacental artery endothelial (oFPAE) cells. Treatment with VEGF stimulated both time- and dose-dependent activation of ERK2/1 in oFPAE cells. VEGF-induced ERK2/1 activation was mediated by VEGFR2, but not VEGFR1, and was linked to intracellular calcium, protein kinase C, and Raf-1. VEGF stimulated oFPAE cell proliferation, migration, and tube formation in vitro. Blockade of ERK2/1 pathway attenuated VEGF-induced cell proliferation and tube formation but failed to inhibit migration in oFPAE cells. Disruption of caveolae by cholesterol depletion with methyl-beta-cyclodextrin or by down-regulation of its structural protein caveolin-1 blunted VEGF-induced ERK2/1 activation, proliferation, and tube formation in oFPAE cells, indicating an essential role of integral caveolae in these VEGF-induced responses. Adenoviral overexpression of caveolin-1 and addition of a caveolin scaffolding domain peptide also inhibited VEGF-stimulated ERK2/1 activation, cell proliferation, and tube formation in oFPAE cells. Furthermore, molecules comprising the ERK2/1 signaling module, including VEGFR2, protein kinase Calpha, Raf-1, MAPK kinase 1/2, and ERK2/1, resided with caveolin-1 in caveolae. VEGF transiently stimulated ERK2/1 activation in the caveolae similarly as in intact cells. Caveolae disruption greatly diminished ERK2/1 activation by VEGF in oFPAE cell caveolae. We conclude that caveolae function as a platform for compartmentalizing the VEGF-induced ERK2/1 signaling module. Caveolin-1 and caveolae play a paradoxical role in regulating VEGF-induced ERK2/1 activation and in vitro angiogenesis as evidenced by the similar inhibitory effects of down-regulation and overexpression of caveolin-1 and disruption of caveolae in oFPAE cells.
Figures







Similar articles
-
Caveolin-1 orchestrates fibroblast growth factor 2 signaling control of angiogenesis in placental artery endothelial cell caveolae.J Cell Physiol. 2012 Jun;227(6):2480-91. doi: 10.1002/jcp.22984. J Cell Physiol. 2012. PMID: 21830216 Free PMC article.
-
Deciphering mechanisms controlling placental artery endothelial cell migration stimulated by vascular endothelial growth factor.Endocrinology. 2010 Jul;151(7):3432-44. doi: 10.1210/en.2009-1305. Epub 2010 May 12. Endocrinology. 2010. PMID: 20463056 Free PMC article.
-
Differential activation of multiple signalling pathways dictates eNOS upregulation by FGF2 but not VEGF in placental artery endothelial cells.Placenta. 2008 Aug;29(8):708-17. doi: 10.1016/j.placenta.2008.05.005. Epub 2008 Jun 20. Placenta. 2008. PMID: 18571718 Free PMC article.
-
Caveolin-1, caveolae, and glioblastoma.Neuro Oncol. 2012 Jun;14(6):679-88. doi: 10.1093/neuonc/nos079. Epub 2012 Apr 16. Neuro Oncol. 2012. PMID: 22508761 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Caveolin-1 and Atherosclerosis: Regulation of LDLs Fate in Endothelial Cells.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 May 17;24(10):8869. doi: 10.3390/ijms24108869. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 37240214 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Regulation of placental angiogenesis.Microcirculation. 2014 Jan;21(1):15-25. doi: 10.1111/micc.12093. Microcirculation. 2014. PMID: 23981199 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Distinct roles of HIF1A in endothelial adaptations to physiological and ambient oxygen.Mol Cell Endocrinol. 2014 Jun 25;391(1-2):60-7. doi: 10.1016/j.mce.2014.04.008. Epub 2014 May 2. Mol Cell Endocrinol. 2014. PMID: 24796659 Free PMC article.
-
Upregulation of MUC5AC by VEGF in human primary bronchial epithelial cells: implications for asthma.Respir Res. 2019 Dec 12;20(1):282. doi: 10.1186/s12931-019-1245-1. Respir Res. 2019. PMID: 31831011 Free PMC article.
-
Rac1-dependent intracellular superoxide formation mediates vascular endothelial growth factor-induced placental angiogenesis in vitro.Endocrinology. 2010 Nov;151(11):5315-25. doi: 10.1210/en.2010-0178. Epub 2010 Sep 15. Endocrinology. 2010. PMID: 20844008 Free PMC article.
-
GNA11 differentially mediates fibroblast growth factor 2- and vascular endothelial growth factor A-induced cellular responses in human fetoplacental endothelial cells.J Physiol. 2018 Jun;596(12):2333-2344. doi: 10.1113/JP275677. Epub 2018 May 12. J Physiol. 2018. PMID: 29659033 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Reynolds LP, Redmer DA 2001 Angiogenesis in the placenta. Biol Reprod 64:1033–1040 - PubMed
-
- Magness RR, Rosenfeld CR 1989 The role of steroid hormones in the control of uterine blood flow. In: Rosenfeld CR, ed. Uterine circulation. Chap 10. Ithaca, NY: Perinatology Press; 239–271
-
- Cross JC, Werb Z, Fisher SJ 1994 Implantation and the placenta: key pieces of the development puzzle. Science 266:1508–1518 - PubMed
-
- Reynolds LP, Killilea SD, Redmer DA 1992 Angiogenesis in the female reproductive system. FASEB J 6:886–892 - PubMed
-
- Leach L, Babawale MO, Anderson M, Lammiman M 2002 Vasculogenesis, angiogenesis and the molecular organisation of endothelial junctions in the early human placenta. J Vasc Res 39:246–259 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

