Modeling stochasticity and robustness in gene regulatory networks
- PMID: 19477975
- PMCID: PMC2687968
- DOI: 10.1093/bioinformatics/btp214
Modeling stochasticity and robustness in gene regulatory networks
Abstract
Motivation: Understanding gene regulation in biological processes and modeling the robustness of underlying regulatory networks is an important problem that is currently being addressed by computational systems biologists. Lately, there has been a renewed interest in Boolean modeling techniques for gene regulatory networks (GRNs). However, due to their deterministic nature, it is often difficult to identify whether these modeling approaches are robust to the addition of stochastic noise that is widespread in gene regulatory processes. Stochasticity in Boolean models of GRNs has been addressed relatively sparingly in the past, mainly by flipping the expression of genes between different expression levels with a predefined probability. This stochasticity in nodes (SIN) model leads to over representation of noise in GRNs and hence non-correspondence with biological observations.
Results: In this article, we introduce the stochasticity in functions (SIF) model for simulating stochasticity in Boolean models of GRNs. By providing biological motivation behind the use of the SIF model and applying it to the T-helper and T-cell activation networks, we show that the SIF model provides more biologically robust results than the existing SIN model of stochasticity in GRNs.
Availability: Algorithms are made available under our Boolean modeling toolbox, GenYsis. The software binaries can be downloaded from http://si2.epfl.ch/ approximately garg/genysis.html.
Figures
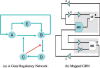

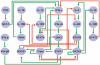


References
-
- Becskei A, Serrano L. Engineering stability in gene networks by autoregulation. Nature. 2000;405:590–593. - PubMed
-
- Bernot G, et al. Application of formal methods to biological regulatory networks: extending Thomas' asynchronous logical approach with temporal logic. J. Theor. Biol. 2004;229:339–347. - PubMed
-
- Bergmann C, van Hemmen JL. Th1 or Th2: how an appropriate T helper response can be made. Bull. Math. Biol. 2001;63:405–430. - PubMed
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

