Speeding up HMM algorithms for genetic linkage analysis via chain reductions of the state space
- PMID: 19477987
- PMCID: PMC2687978
- DOI: 10.1093/bioinformatics/btp224
Speeding up HMM algorithms for genetic linkage analysis via chain reductions of the state space
Abstract
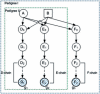
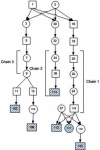
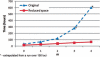
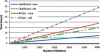
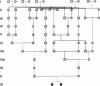
We develop an hidden Markov model (HMM)-based algorithm for computing exact parametric and non-parametric linkage scores in larger pedigrees than was possible before. The algorithm is applicable whenever there are chains of persons in the pedigree with no genetic measurements and with unknown affection status. The algorithm is based on shrinking the state space of the HMM considerably using such chains. In a two g-degree cousins pedigree the reduction drops the state space from being exponential in g to being linear in g. For a Finnish family in which two affected children suffer from a rare cold-inducing sweating syndrome, we were able to reduce the state space by more than five orders of magnitude from 2(50) to 2(32). In another pedigree of state-space size of 2(27), used for a study of pituitary adenoma, the state space reduced by a factor of 8.5 and consequently exact linkage scores can now be computed, rather than approximated.
Supplementary information: Supplementary data are available at Bioinformatics online.
Figures
References
-
- Abecasis GR, et al. Merlin-rapid analysis of dense genetic maps using sparse gene flow trees. Nat. Genet. 2002;30:97–101. - PubMed
-
- Dechter R. Bucket elimination: a unifying framework for probabilistic inference. In: Jordan MI, editor. Learning in Graphical Models. Kluwer Academic Press; 1998. pp. 75–104.
-
- Elston R, Stewart J. A general model for the analysis of pedigree data. Hum. Hered. 1971;21:523–542. - PubMed

