Disease mutations in the human mitochondrial DNA polymerase thumb subdomain impart severe defects in mitochondrial DNA replication
- PMID: 19478085
- PMCID: PMC2740576
- DOI: 10.1074/jbc.M109.011940
Disease mutations in the human mitochondrial DNA polymerase thumb subdomain impart severe defects in mitochondrial DNA replication
Abstract
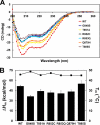
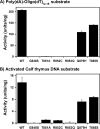
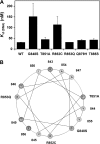
Forty-five different point mutations in POLG, the gene encoding the catalytic subunit of the human mitochondrial DNA polymerase (pol gamma), cause the early onset mitochondrial DNA depletion disorder, Alpers syndrome. Sequence analysis of the C-terminal polymerase region of pol gamma revealed a cluster of four Alpers mutations at highly conserved residues in the thumb subdomain (G848S, c.2542g-->a; T851A, c.2551a-->g; R852C, c.2554c-->t; R853Q, c.2558g-->a) and two Alpers mutations at less conserved positions in the adjacent palm subdomain (Q879H, c.2637g-->t and T885S, c.2653a-->t). Biochemical characterization of purified, recombinant forms of pol gamma revealed that Alpers mutations in the thumb subdomain reduced polymerase activity more than 99% relative to the wild-type enzyme, whereas the palm subdomain mutations retained 50-70% wild-type polymerase activity. All six mutant enzymes retained physical and functional interaction with the pol gamma accessory subunit (p55), and none of the six mutants exhibited defects in misinsertion fidelity in vitro. However, differential DNA binding by these mutants suggests a possible orientation of the DNA with respect to the polymerase during catalysis. To our knowledge this study represents the first structure-function analysis of the thumb subdomain in pol gamma and examines the consequences of mitochondrial disease mutations in this region.
Figures

References
-
- Kaguni L. S. (2004) Annu. Rev. Biochem. 73, 293–320 - PubMed
-
- Graziewicz M. A., Longley M. J., Copeland W. C. (2006) Chem. Rev. 106, 383–405 - PubMed
-
- Yakubovskaya E., Chen Z., Carrodeguas J. A., Kisker C., Bogenhagen D. F. (2006) J. Biol. Chem. 281, 374–382 - PubMed
-
- Lim S. E., Longley M. J., Copeland W. C. (1999) J. Biol. Chem. 274, 38197–38203 - PubMed
-
- Johnson A. A., Tsai Y., Graves S. W., Johnson K. A. (2000) Biochemistry 39, 1702–1708 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

