Aberrantly glycosylated IgA1 in IgA nephropathy patients is recognized by IgG antibodies with restricted heterogeneity
- PMID: 19478457
- PMCID: PMC2689118
- DOI: 10.1172/JCI38468
Aberrantly glycosylated IgA1 in IgA nephropathy patients is recognized by IgG antibodies with restricted heterogeneity
Abstract
IgA nephropathy (IgAN) is characterized by circulating immune complexes composed of galactose-deficient IgA1 and a glycan-specific IgG antibody. These immune complexes deposit in the glomerular mesangium and induce the mesangioproliferative glomerulonephritis characteristic of IgAN. To define the precise specificities and molecular properties of the IgG antibodies, we generated EBV-immortalized IgG-secreting lymphocytes from patients with IgAN and found that the secreted IgG formed complexes with galactose-deficient IgA1 in a glycan-dependent manner. We cloned and sequenced the heavy- and light-chain antigen-binding domains of IgG specific for galactose-deficient IgA1 and identified an A to S substitution in the complementarity-determining region 3 of the variable region of the gene encoding the IgG heavy chain in IgAN patients. Furthermore, site-directed mutagenesis that reverted the residue to alanine reduced the binding of recombinant IgG to galactose-deficient IgA1. Finally, we developed a dot-blot assay for the glycan-specific IgG antibody that differentiated patients with IgAN from healthy and disease controls with 88% specificity and 95% sensitivity and found that elevated levels of this antibody in the sera of patients with IgAN correlated with proteinuria. Collectively, these findings indicate that glycan-specific antibodies are associated with the development of IgAN and may represent a disease-specific marker and potential therapeutic target.
Figures
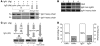
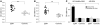
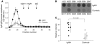
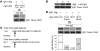

Comment in
-
Analyzing antibody activity in IgA nephropathy.J Clin Invest. 2009 Jun;119(6):1450-2. doi: 10.1172/jci39189. J Clin Invest. 2009. PMID: 19504718 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- DK082753/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R21 DK075868/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- DK080301/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- 1UL1RR025777-01/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DK078244/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- DK071802/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- M01 RR000211/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 RR025777/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DK071802/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- DK075868/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- DK077279/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- DK064400/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- M01 RR00211/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- R24 DK064400/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R21 DK080301/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- DK061525/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DK082753/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- DK078244/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- P01 DK061525/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R56 DK078244/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R21 DK077279/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

