Localisation of DivIVA by targeting to negatively curved membranes
- PMID: 19478798
- PMCID: PMC2690451
- DOI: 10.1038/emboj.2009.129
Localisation of DivIVA by targeting to negatively curved membranes
Abstract
DivIVA is a conserved protein in Gram-positive bacteria and involved in various processes related to cell growth, cell division and spore formation. DivIVA is specifically targeted to cell division sites and cell poles. In Bacillus subtilis, DivIVA helps to localise other proteins, such as the conserved cell division inhibitor proteins, MinC/MinD, and the chromosome segregation protein, RacA. Little is known about the mechanism that localises DivIVA. Here we show that DivIVA binds to liposomes, and that the N terminus harbours the membrane targeting sequence. The purified protein can stimulate binding of RacA to membranes. In mutants with aberrant cell shapes, DivIVA accumulates where the cell membrane is most strongly curved. On the basis of electron microscopic studies and other data, we propose that this is due to molecular bridging of the curvature by DivIVA multimers. This model may explain why DivIVA localises at cell division sites. A Monte-Carlo simulation study showed that molecular bridging can be a general mechanism for binding of proteins to negatively curved membranes.
Figures

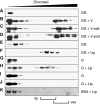

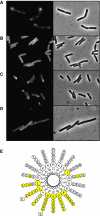
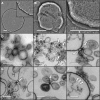
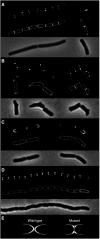

Comment in
-
Irresistible curves.EMBO J. 2009 Aug 5;28(15):2147-8. doi: 10.1038/emboj.2009.167. EMBO J. 2009. PMID: 19654604 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
-
- Allen MP, Tildesley DJ (1989) Computer Simulation of Liquids. Oxford: Oxford University Press
-
- Anderluh G, Besenicar M, Kladnik A, Lakey JH, Macek P (2005) Properties of nonfused liposomes immobilized on an L1 Biacore chip and their permeabilization by a eukaryotic pore-forming toxin. Anal Biochem 344: 43–52 - PubMed
-
- Ben-Yehuda S, Rudner DZ, Losick R (2003) RacA, a bacterial protein that anchors chromosomes to the cell poles. Science 299: 532–536 - PubMed
-
- Binder K, Heermann D (2002) Monte Carlo Simulation in Statistical Physics: An Introduction, 4th edn. Berlin: Springer-Verlag.
-
- Bramkamp M, Emmins R, Weston L, Donovan C, Daniel RA, Errington J (2008) A novel component of the division-site selection system of Bacillus subtilis and a new mode of action for the division inhibitor MinCD. Mol Microbiol 70: 1556–1569 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

