Immunological interactions between 2 common pathogens, Th1-inducing protozoan Toxoplasma gondii and the Th2-inducing helminth Fasciola hepatica
- PMID: 19478853
- PMCID: PMC2682559
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0005692
Immunological interactions between 2 common pathogens, Th1-inducing protozoan Toxoplasma gondii and the Th2-inducing helminth Fasciola hepatica
Abstract
Background: The nature of the immune response to infection is dependent on the type of infecting organism. Intracellular organisms such as Toxoplasma gondii stimulate a Th1-driven response associated with production of IL-12, IFN-gamma, nitric oxide and IgG2a antibodies and classical activation of macrophages. In contrast, extracellular helminths such as Fasciola hepatica induce Th2 responses characterised by the production of IL-4, IL-5, IL-10 and IgG1 antibodies and alternative activation of macrophages. As co-infections with these types of parasites commonly exist in the field it is relevant to examine how the various facets of the immune responses induced by each may influence or counter-regulate that of the other.
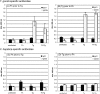
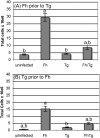
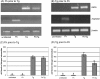
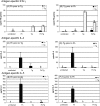
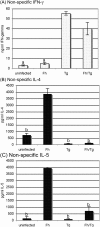
Principal findings: Regardless, of whether F. hepatica infection preceded or succeeded T. gondii infection, there was little impact on the production of the Th1 cytokines IL-12, IFN-gamma or on the development of classically-activated macrophages induced by T. gondii. By contrast, the production of helminth-specific Th2 cytokines, such as IL-4 and IL-5, was suppressed by infection with T. gondii. Additionally, the recruitment and alternative activation of macrophages by F. hepatica was blocked or reversed by subsequent infection with T. gondii. The clinical symptoms of toxoplasmosis and the survival rate of infected mice were not significantly altered by the helminth.
Conclusions: Despite previous studies showing that F. hepatica suppressed the classical activation of macrophages and the Th1-driven responses of mice to bystander microbial infection, as well as reduced their ability to reject these, here we found that the potent immune responses to T. gondii were capable of suppressing the responses to helminth infection. Clearly, the outcome of particular infections in polyparasitoses depends on the means and potency by which each pathogen controls the immune response.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
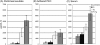
Similar articles
-
Toxoplasma Co-infection Prevents Th2 Differentiation and Leads to a Helminth-Specific Th1 Response.Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2017 Jul 25;7:341. doi: 10.3389/fcimb.2017.00341. eCollection 2017. Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2017. PMID: 28791259 Free PMC article.
-
Fasciola hepatica infection downregulates Th1 responses in mice.Parasite Immunol. 2000 Mar;22(3):147-55. doi: 10.1046/j.1365-3024.2000.00290.x. Parasite Immunol. 2000. PMID: 10672196
-
Infection with a helminth parasite attenuates autoimmunity through TGF-beta-mediated suppression of Th17 and Th1 responses.J Immunol. 2009 Aug 1;183(3):1577-86. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.0803803. Epub 2009 Jul 8. J Immunol. 2009. PMID: 19587018
-
Alternatively activated macrophages in helminth infections.Curr Opin Immunol. 2007 Aug;19(4):448-53. doi: 10.1016/j.coi.2007.07.002. Epub 2007 Aug 16. Curr Opin Immunol. 2007. PMID: 17702561 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Insights into inflammatory bowel disease using Toxoplasma gondii as an infectious trigger.Immunol Cell Biol. 2012 Aug;90(7):668-75. doi: 10.1038/icb.2011.93. Epub 2011 Nov 8. Immunol Cell Biol. 2012. PMID: 22064707 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Main Cardiac Histopathologic Alterations in the Acute Phase of Trypanosoma cruzi Infection in a Murine Model.Pathogens. 2023 Aug 26;12(9):1084. doi: 10.3390/pathogens12091084. Pathogens. 2023. PMID: 37764892 Free PMC article.
-
Toxoplasma gondii Suppresses Th2-Induced by Trichinella spiralis Infection and Downregulates Serine Protease Genes Expression: A Critical Role in Vaccine Development.Iran J Parasitol. 2023 Apr-Jun;18(2):172-181. doi: 10.18502/ijpa.v18i2.13183. Iran J Parasitol. 2023. PMID: 37583627 Free PMC article.
-
Significance of a common 65 kDa antigen in the experimental fasciolosis and toxoplasmosis.J Parasit Dis. 2015 Sep;39(3):550-6. doi: 10.1007/s12639-013-0394-2. Epub 2013 Nov 20. J Parasit Dis. 2015. PMID: 26345069 Free PMC article.
-
Sexual Dimorphism of the Neuroimmunoendocrine Response in the Spleen during a Helminth Infection: A New Role for an Old Player?Pathogens. 2022 Mar 1;11(3):308. doi: 10.3390/pathogens11030308. Pathogens. 2022. PMID: 35335632 Free PMC article.
-
What is the price of neglecting parasite groups when assessing the cost of co-infection?Epidemiol Infect. 2014 Jul;142(7):1533-40. doi: 10.1017/S0950268813002100. Epub 2013 Sep 16. Epidemiol Infect. 2014. PMID: 24040768 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Jankovic D, Liu Z, Gause WC. Th1- and Th2-cell commitment during infectious disease: asymmetry in divergent pathways. Trends in Immunology. 2001;22:450–457. - PubMed
-
- Mulcahy G, Joyce P, Dalton JP. J.P. Dalton, ed. Fasciolosis. CABI Publishing; 1999. Immunology of Fasciola hepatica infection. pp. 341–375.
-
- O' Neill S, Brady MT, Callanan JJ, Mulcahy G, Joyce P. Fasciola hepatica infection downregulates Th1 responses in mice. Parasite Immunology. 2000;22:147–155. - PubMed
-
- O'Neill S, Mills KHG, Dalton JP. Fasciola hepatica cathepsin L cysteine proteinase suppresses Bordetella pertussis-specific interferon-γ production in vivo. Parasite Immunol. 2001;23:541–547. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

