The Base Excision Repair system of Salmonella enterica serovar typhimurium counteracts DNA damage by host nitric oxide
- PMID: 19478870
- PMCID: PMC2680585
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.ppat.1000451
The Base Excision Repair system of Salmonella enterica serovar typhimurium counteracts DNA damage by host nitric oxide
Abstract
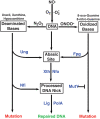
Intracellular pathogens must withstand nitric oxide (NO.) generated by host phagocytes. Salmonella enterica serovar Typhimurium interferes with intracellular trafficking of inducible nitric oxide synthase (iNOS) and possesses multiple systems to detoxify NO.. Consequently, the level of NO. stress encountered by S. Typhimurium during infection in vivo has been unknown. The Base Excision Repair (BER) system recognizes and repairs damaged DNA bases including cytosine and guanine residues modified by reactive nitrogen species. Apurinic/apyrimidinic (AP) sites generated by BER glycosylases require subsequent processing by AP endonucleases. S. Typhimurium xth nfo mutants lacking AP endonuclease activity exhibit increased NO. sensitivity resulting from chromosomal fragmentation at unprocessed AP sites. BER mutant strains were thus used to probe the nature and extent of nitrosative damage sustained by intracellular bacteria during infection. Here we show that an xth nfo S. Typhimurium mutant is attenuated for virulence in C3H/HeN mice, and virulence can be completely restored by the iNOS inhibitor L-NIL. Inactivation of the ung or fpg glycosylase genes partially restores virulence to xth nfo mutant S. Typhimurium, demonstrating that NO. fluxes in vivo are sufficient to modify cytosine and guanine bases, respectively. Mutants lacking ung or fpg exhibit NO.-dependent hypermutability during infection, underscoring the importance of BER in protecting Salmonella from the genotoxic effects of host NO.. These observations demonstrate that host-derived NO. damages Salmonella DNA in vivo, and the BER system is required to maintain bacterial genomic integrity.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures


References
-
- DeGroote MA, Fang FC. Antimicrobial Properties of Nitric Oxide. In: Fang FC, editor. Nitric Oxide and Infection. New York: Kluwer Academic/Plenum Publishers; 1999. pp. 231–247.
-
- Fang FC. Antimicrobial reactive oxygen and nitrogen species: concepts and controversies. Nat Rev Microbiol. 2004;2:820–832. - PubMed
-
- Espey MG, Miranda KM, Pluta RM, Wink DA. Nitrosative capacity of macrophages is dependent on nitric-oxide synthase induction signals. J Biol Chem. 2000;275:11341–11347. - PubMed
-
- Butler AR, Megson IL. Non-heme iron nitrosyls in biology. Chem Rev. 2002;102:1155–1166. - PubMed
-
- Cooper CE. Nitric oxide and iron proteins. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1999;1411:290–309. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

