A biphasic oxidation of alcohols to aldehydes and ketones using a simplified packed-bed microreactor
- PMID: 19478910
- PMCID: PMC2686313
- DOI: 10.3762/bjoc.5.17
A biphasic oxidation of alcohols to aldehydes and ketones using a simplified packed-bed microreactor
Abstract
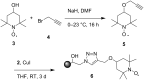
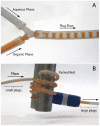
We demonstrate the preparation and characterization of a simplified packed-bed microreactor using an immobilized TEMPO catalyst shown to oxidize primary and secondary alcohols via the biphasic Anelli-Montanari protocol. Oxidations occurred in high yields with great stability over time. We observed that plugs of aqueous oxidant and organic alcohol entered the reactor as plugs but merged into an emulsion on the packed-bed. The emulsion coalesced into larger plugs upon exiting the reactor, leaving the organic product separate from the aqueous by-products. Furthermore, the microreactor oxidized a wide range of alcohols and remained active in excess of 100 trials without showing any loss of catalytic activity.
Keywords: TEMPO; alcohol oxidation; flow chemistry; heterogeneous catalysis; microreactors.
Figures


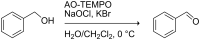

References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
