The role of IL-1 in the pathogenesis of heart disease
- PMID: 19479203
- PMCID: PMC2788964
- DOI: 10.1007/s00005-009-0024-y
The role of IL-1 in the pathogenesis of heart disease
Abstract
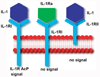
Interleukin (IL)-1 consists of two distinct ligands, IL-1alpha and IL-1beta, with indistinguishable biological activities that signal through the IL-1 type I receptor (IL-1RI). A naturally occurring IL-1 receptor antagonist (IL-1Ra) binds to IL-1RI without initiating signal transduction and prevents IL-1 signaling, competitively inhibiting IL-1-mediated responses. Emerging evidence suggests that the balance between IL-1 agonists and antagonists plays an essential role in a variety of cardiovascular conditions. IL-1 may play a role in atherothrombotic disease by promoting the formation of atheromatous lesions, enhancing vascular inflammation, and triggering plaque destabilization. Following myocardial infarction, IL-1 critically regulates the inflammatory response and is involved in the development of adverse remodeling by enhancing expression of matrix metalloproteinases. IL-1 signaling may also be an essential mediator in the pathogenesis of heart failure by suppressing cardiac contractility, promoting myocardial hypertrophy, and inducing cardiomyocyte apoptosis. The present review summarizes current available data showing the significant role of IL-1 signaling in heart disease and raising the possibility that IL-1 inhibitors (such as anakinra, a nonglycosylated recombinant human IL-1Ra) may be clinically useful agents in patients with certain cardiovascular conditions.
Figures
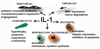
References
-
- Abbate A, Salloum FN, Vecile E, Das A, Hoke NN, Straino S, Biondi-Zoccai GG, Houser JE, Qureshi IZ, Ownby ED, Gustini E, Biasucci LM, Severino A, Capogrossi MC, Vetrovec GW, Crea F, Baldi A, Kukreja RC, Dobrina A. Anakinra, a recombinant human interleukin-1 receptor antagonist, inhibits apoptosis in experimental acute myocardial infarction. Circulation. 2008;117:2670–2683. - PubMed
-
- Allan SM, Tyrrell PJ, Rothwell NJ. Interleukin-1 and neuronal injury. Nat Rev Immunol. 2005;5:629–640. - PubMed
-
- Apostolakis S, Vogiatzi K, Krambovitis E, Spandidos DA. IL-1 cytokines in cardiovascular disease: diagnostic, prognostic and therapeutic implications. Cardiovasc Hematol Agents Med Chem. 2008;6:150–158. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

