Neurofibromin physically interacts with the N-terminal domain of focal adhesion kinase
- PMID: 19479903
- PMCID: PMC2783617
- DOI: 10.1002/mc.20552
Neurofibromin physically interacts with the N-terminal domain of focal adhesion kinase
Abstract
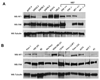
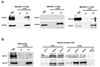
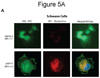
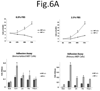
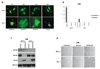
The NF1 gene that is altered in patients with type 1 neurofibromatosis (NF1) encodes a neurofibromin protein that functions as a tumor suppressor. In this report, we show for the first time physical interaction between neurofibromin and focal adhesion kinase (FAK), the protein that localizes at focal adhesions. We show that neurofibromin associates with the N-terminal domain of FAK, and that the C-terminal domain of neurofibromin directly interacts with FAK. Confocal microscopy demonstrates colocalization of NF1 and FAK in the cytoplasm, perinuclear and nuclear regions inside the cells. Nf1+/+ MEF cells expressed less cell growth during serum deprivation conditions, and adhered less on collagen and fibronectin-treated plates than Nf1(-/-) MEF cells, associated with changes in actin and FAK staining. In addition, Nf1+/+ MEF cells detached more significantly than Nf1(-/-) MEF cells by disruption of FAK signaling with the dominant-negative inhibitor of FAK, C-terminal domain of FAK (FAK-CD). Thus, the results demonstrate the novel interaction of neurofibromin and FAK and suggest their involvement in cell adhesion, cell growth, and other cellular events and pathways.
Figures





Similar articles
-
Direct interaction of the N-terminal domain of focal adhesion kinase with the N-terminal transactivation domain of p53.J Biol Chem. 2005 Jul 1;280(26):25008-21. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M414172200. Epub 2005 Apr 25. J Biol Chem. 2005. PMID: 15855171
-
NF1 modulates the effects of Ras oncogenes: evidence of other NF1 function besides its GAP activity.J Cell Physiol. 2003 Nov;197(2):214-24. doi: 10.1002/jcp.10349. J Cell Physiol. 2003. PMID: 14502561
-
Neurofibromatosis type 1 (NF1) tumor suppressor, neurofibromin, regulates the neuronal differentiation of PC12 cells via its associating protein, CRMP-2.J Biol Chem. 2008 Apr 4;283(14):9399-413. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M708206200. Epub 2008 Jan 23. J Biol Chem. 2008. PMID: 18218617
-
Focal adhesion kinase versus p53: apoptosis or survival?Sci Signal. 2008 May 20;1(20):pe22. doi: 10.1126/stke.120pe22. Sci Signal. 2008. PMID: 18493017 Free PMC article. Review.
-
[Neurofibromin - protein structure and cellular functions in the context of neurofibromatosis type I pathogenesis].Postepy Hig Med Dosw (Online). 2015 Dec 9;69:1331-48. doi: 10.5604/17322693.1185213. Postepy Hig Med Dosw (Online). 2015. PMID: 26671924 Review. Polish.
Cited by
-
Comparative oncogenomics implicates the neurofibromin 1 gene (NF1) as a breast cancer driver.Genetics. 2012 Oct;192(2):385-96. doi: 10.1534/genetics.112.142802. Epub 2012 Jul 30. Genetics. 2012. PMID: 22851646 Free PMC article.
-
Drug Responses in Plexiform Neurofibroma Type I (PNF1) Cell Lines Using High-Throughput Data and Combined Effectiveness and Potency.Cancers (Basel). 2023 Dec 12;15(24):5811. doi: 10.3390/cancers15245811. Cancers (Basel). 2023. PMID: 38136356 Free PMC article.
-
From neurodevelopment to neurodegeneration: the interaction of neurofibromin and valosin-containing protein/p97 in regulation of dendritic spine formation.J Biomed Sci. 2012 Mar 26;19(1):33. doi: 10.1186/1423-0127-19-33. J Biomed Sci. 2012. PMID: 22449146 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The therapeutic potential of neurofibromin signaling pathways and binding partners.Commun Biol. 2023 Apr 20;6(1):436. doi: 10.1038/s42003-023-04815-0. Commun Biol. 2023. PMID: 37081086 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The NF1 gene revisited - from bench to bedside.Oncotarget. 2014 Aug 15;5(15):5873-92. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.2194. Oncotarget. 2014. PMID: 25026295 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Wallace MR, Marchuk DA, Andersen LB, et al. Type 1 neurofibromatosis gene: identification of a large transcript disrupted in three NF1 patients. Science. 1990;249:181–189. - PubMed
-
- Marchuk DA, Saulino AM, Tavakkol R, et al. cDNA cloning of the type 1 neurofibromatosis gene: complete sequence of the NF1 gene product. Genomics. 1991;11:931–940. - PubMed
-
- Daston MM, Scrable H, Nordlund M, Sturbaum AK, Nissen LM, Ratner N. The protein product of the neurofibromatosis type 1 gene is expressed at highest abundance in neurons, Schwann cells, and oligodendrocytes. Neuron. 1992;8:415–428. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

