Validity of low copy number typing and applications to forensic science
- PMID: 19480017
- PMCID: PMC2702736
- DOI: 10.3325/cmj.2009.50.207
Validity of low copy number typing and applications to forensic science
Abstract
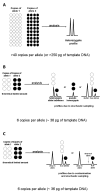
Low copy number (LCN) typing, particularly for current short tandem repeat (STR) typing, refers to the analysis of any sample that contains less than 200 pg of template DNA. Generally, LCN typing simply can be defined as the analysis of any DNA sample where the results are below the stochastic threshold for reliable interpretation. There are a number of methodologies to increase sensitivity of detection to enable LCN typing. These approaches encompass modifications during the polymerase chain reaction (PCR) and/or post-PCR manipulations. Regardless of the manipulations, when processing a small number of starting templates during the PCR exaggerated stochastic sampling effects will occur. The result is that several phenomena can occur: a substantial imbalance of 2 alleles at a given heterozygous locus, allelic dropout, or increased stutter. With increased sensitivity of detection there is a concomitant increased risk of contamination. Recently, a commission reviewed LCN typing and found it to be "robust" and "fit for purpose." Because LCN analysis by its nature is not reproducible, it cannot be considered as robust as that associated with conventional DNA typing. The findings of the commission seem inconsistent with the nature of LCN typing. While LCN typing is appropriate for identification of missing persons and human remains and for developing investigative leads, caution should be taken with its use in other endeavors until developments are made that overcome the vagaries of LCN typing. A more in-depth evaluation by the greater scientific community is warranted. The issues to consider include: training and education, evidence handling and collection procedures, the application or purpose for which the LCN result will be used, the reliability of current LCN methods, replicate analyses, interpretation and uncertainty, report writing, validation requirements, and alternate methodologies for better performance.
Figures

References
-
- Collins PJ, Hennessy LK, Leibelt CS, Roby RK, Reeder DJ, Foxall PA. Developmental validation of a single-tube amplification of the 13 CODIS STR loci, D2S1338, D19S433, and amelogenin: the AmpFlSTR Identifiler PCR Amplification Kit. J Forensic Sci. 2004;49:1265–77. doi: 10.1520/JFS2002195. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Krenke BE, Tereba A, Anderson SJ, Buel E, Culhane S, Finis CJ, et al. Validation of a 16-locus fluorescent multiplex system. J Forensic Sci. 2002;47:773–85. - PubMed
-
- Holt CL, Buoncristiani M, Wallin JM, Nguyen T, Lazaruk KD, Walsh PS. TWGDAM validation of AmpFlSTR PCR amplification kits for forensic DNA casework. J Forensic Sci. 2002;47:66–96. - PubMed
-
- Micka KA, Amiott EA, Hockenberry TL, Sprecher CJ, Lins AM, Rabbach DR, et al. TWGDAM validation of a nine-locus and a four-locus fluorescent STR multiplex system. J Forensic Sci. 1999;44:1243–57. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

