Application of multivariate statistical procedures to identify transcription factors that correlate with MRP2, 3, and 4 mRNA in adult human livers
- PMID: 19480556
- PMCID: PMC2698955
- DOI: 10.1080/00498250902952514
Application of multivariate statistical procedures to identify transcription factors that correlate with MRP2, 3, and 4 mRNA in adult human livers
Abstract
Multidrug resistance-associated proteins 2-4 (MRP2-4) are membrane efflux transporters critical for the hepatic clearance of pharmaceuticals and endogenous chemicals. Little is known about the constitutive regulation of MRP2-4 mRNA in normal human liver. The purpose of this study was to identify transcription factors whose expression significantly correlates with MRP2-4 mRNA in human liver specimens. Ninety adult human livers were profiled for mRNA expression of MRP2-4 as well as aryl hydrocarbon receptor (AhR), constitutive androstane receptor (CAR), pregnane X receptor (PXR), peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor alpha (PPAR alpha) and gamma (gamma), liver X receptor alpha (LXR alpha), farnesoid X receptor (FXR), glucocorticoid receptor (GR), retinoid X receptor alpha (RXR alpha), hepatocyte nuclear factor 1 alpha (HNF1 alpha) and 4 alpha (4 alpha), and nuclear factor E2-related factor 2 (Nrf2) transcription factors. Using linear regression and stepwise selection of partial R(2)-values, CAR, HNF1 alpha, and PPAR alpha mRNA exhibited the greatest correlation with MRP2, 3, and 4, respectively. Interindividual variation in the expression of the identified transcription factors may account for the variability in constitutive mRNA levels of MRP2-4. The multivariate approach presented in this study should aid in predicting signalling pathways that participate either directly or indirectly in regulating hepatic drug disposition.
Figures

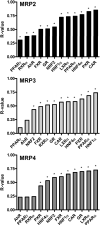

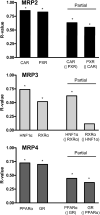
References
-
- Cereghini S. Liver-enriched transcription factors and hepatocyte differentiation. FASEB J. 1996;10:267–282. - PubMed
-
- de la Fuente A, Bing N, Hoeschele I, Mendes P. Discovery of meaningful associations in genomic data using partial correlation coefficients. Bioinformatics. 2004;20:3565–3574. - PubMed
-
- Flavell DM, Ireland H, Stephens JW, Hawe E, Acharya J, Mather H, Hurel SJ, Humphries SE. Peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor alpha gene variation influences age of onset and progression of type 2 diabetes. Diabetes. 2005;54:582–586. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
