Effect of buspirone on thermal sensory and pain thresholds in human volunteers
- PMID: 19480657
- PMCID: PMC2698897
- DOI: 10.1186/1472-6904-9-12
Effect of buspirone on thermal sensory and pain thresholds in human volunteers
Abstract
Background: Buspirone is a partial 5-HT1A receptor agonist. Animal studies have shown that modulation of serotoninergic transmission at the 5-HT1A receptor can induce analgesia in acute pain models. However, no studies have been published so far on the effects of serotonin receptor agonists on pain perception in humans.
Methods: The effects of buspirone (30 mg p.o.) on thermal sensory and pain thresholds were investigated in twelve female volunteers (26 +/- 2 yrs) in a prospective, randomized, double-blind, double-dummy, placebo-controlled study with morphine (10 mg i.v.) as positive control.
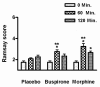
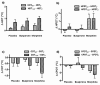
Results: Morphine significantly increased the heat pain detection threshold (DeltaT: placebo 1.0 degrees C and 1.3 degrees C, p < 0.05) at 60 minutes. Buspirone caused mild sedation in six participants at 60 minutes, but was without effect on any of the measured parameters.
Conclusion: Buspirone in the maximal recommended dose was without significant effect on thermal pain. However, as it is only a partial agonist at the 5-HT1A receptor and also acts on other receptor types, the negative results of the present study do not rule out a possible analgesic effect of more specific 5-HT1A receptor agonists.
Figures
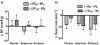
Similar articles
-
5-HT1A agonists induce central cholinergic antinociception.Pharmacol Biochem Behav. 1997 Aug;57(4):835-41. doi: 10.1016/s0091-3057(96)00401-7. Pharmacol Biochem Behav. 1997. PMID: 9259013
-
Modulatory effect of the 5-HT1A agonist buspirone and the mixed non-hallucinogenic 5-HT1A/2A agonist ergotamine on psilocybin-induced psychedelic experience.Eur Neuropsychopharmacol. 2016 Apr;26(4):756-66. doi: 10.1016/j.euroneuro.2016.01.005. Epub 2016 Jan 22. Eur Neuropsychopharmacol. 2016. PMID: 26875114 Clinical Trial.
-
The partial 5-hydroxytryptamine1A receptor agonist buspirone does not antagonize morphine-induced respiratory depression in humans.Clin Pharmacol Ther. 2007 Jan;81(1):59-68. doi: 10.1038/sj.clpt.6100018. Clin Pharmacol Ther. 2007. PMID: 17186000 Clinical Trial.
-
Human motoneurone excitability is depressed by activation of serotonin 1A receptors with buspirone.J Physiol. 2017 Mar 1;595(5):1763-1773. doi: 10.1113/JP273200. Epub 2016 Dec 17. J Physiol. 2017. PMID: 27859267 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Serotonin-1A receptor dependent modulation of pain and reward for improving therapy of chronic pain.Pharmacol Res. 2018 Aug;134:212-219. doi: 10.1016/j.phrs.2018.06.030. Epub 2018 Jun 30. Pharmacol Res. 2018. PMID: 29969666 Review.
Cited by
-
Psychopharmacological characterisation of the successive negative contrast effect in rats.Psychopharmacology (Berl). 2015 Aug;232(15):2697-709. doi: 10.1007/s00213-015-3905-2. Epub 2015 Mar 21. Psychopharmacology (Berl). 2015. PMID: 25791190 Free PMC article.
-
Effect of tonic pain on the corticosterone level in rat pups of various ages subjected to prenatal stress and opportunities for correction of stress-induced impairments.Dokl Biol Sci. 2013 May;450:134-8. doi: 10.1134/S0012496613030204. Epub 2013 Jul 3. Dokl Biol Sci. 2013. PMID: 23821050 No abstract available.
-
Evaluation of sesamol and buspirone in stress induced anxiety in mice.Indian J Pharmacol. 2013 Jan-Feb;45(1):49-53. doi: 10.4103/0253-7613.106435. Indian J Pharmacol. 2013. PMID: 23543858 Free PMC article.
-
Long-Term Effects of Chronic Buspirone during Adolescence Reduce the Adverse Influences of Neonatal Inflammatory Pain and Stress on Adaptive Behavior in Adult Male Rats.Front Behav Neurosci. 2017 Jan 26;11:11. doi: 10.3389/fnbeh.2017.00011. eCollection 2017. Front Behav Neurosci. 2017. PMID: 28184190 Free PMC article.
-
Buspirone alleviates anxiety, depression, and colitis; and modulates gut microbiota in mice.Sci Rep. 2021 Mar 17;11(1):6094. doi: 10.1038/s41598-021-85681-w. Sci Rep. 2021. PMID: 33731795 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Besson JM, Chaouch A. Peripheral and spinal mechanisms of nociception. Physiol Rev. 1987;67:67–186. - PubMed
-
- Colpaert FC, Tarayre JP, Koek W, Pauwels PJ, Bardin L, Xu XJ, Wiesenfeld-Hallin Z, Cosi C, Carilla-Durand E, Assie MB, et al. Large-amplitude 5-HT1A receptor activation: a new mechanism of profound, central analgesia. Neuropharmacology. 2002;43:945–958. doi: 10.1016/S0028-3908(02)00119-3. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Palm F, Mossner R, Chen Y, He L, Gerlach M, Bischofs S, Riederer P, Lesch KP, Sommer C. Reduced thermal hyperalgesia and enhanced peripheral nerve injury after hind paw inflammation in mice lacking the serotonin-transporter. Eur J Pain. 2008;12:790–797. doi: 10.1016/j.ejpain.2007.11.009. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Kayser V, Elfassi IE, Aubel B, Melfort M, Julius D, Gingrich JA, Hamon M, Bourgoin S. Mechanical, thermal and formalin-induced nociception is differentially altered in 5-HT1A-/-, 5-HT1B-/-, 5-HT2A-/-, 5-HT3A-/- and 5-HTT-/- knock-out male mice. Pain. 2007;130:235–248. doi: 10.1016/j.pain.2006.11.015. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

