Rapid diagnosis of spinal muscular atrophy using high-resolution melting analysis
- PMID: 19480685
- PMCID: PMC2694785
- DOI: 10.1186/1471-2350-10-45
Rapid diagnosis of spinal muscular atrophy using high-resolution melting analysis
Abstract
Background: Spinal muscular atrophy (SMA) is an autosomal recessive hereditary disorder caused by mutations of the survival motor neuron 1 (SMN1) gene. Recently, high-resolution DNA melting analysis (HRMA) with saturation LC Green dyes has become a powerful post-PCR technique for genotyping or mutation scanning. So far, no studies have applied HRMA to the molecular analysis of SMA.
Methods: The exon 7 and the flanking area of the SMN1 and SMN2 genes of 55 SMA patients and 46 unrelated normal individuals were amplified with asymmetric PCR with unlabeled probe and symmetric PCR without probe, respectively. The saturation LC Green dyes were added to the PCR system. The PCR products were loaded onto the LightScanner system and were melted from 60 degrees C to 95 degrees C slowly. The melting curves were acquired and analyzed by the LightScanner software.
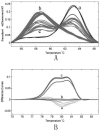
Results: Three types of melting curves that correlated with the presumed genotype of SMA patients and controls were clearly separated on the HRMA chromatogram with the unlabeled probe. The 55 SMA patients and 46 non-SMA controls were identified with HRMA with a 100% clinical sensitivity.
Conclusion: The HRMA with saturation LC Green dyes and unlabeled probe appears to be a suitable, alternative method for the diagnosis of SMA, with high sensitivity and specificity.
Figures
References
-
- Wu ZY, Wang N, Mu-Rong SX, Lin MT. Using polymerase chain reaction single strand conformation polymorphism to detect SMNT gene deletions and to confirm clinical diagnosis of spinal muscular atrophy in Chinese. Chin J Neurol. 1998;31:289–291.
-
- Feldkotter M, Schwarzer V, Wirth R, Wienker TF, Wirth B. Quantitative analysis of SMN1 and SMN2 based on real-time lightcycler PCR: fast and highly reliable carrier testing and prediction of severity of spinal muscular atrophy. Am J Hum Genet. 2002;70:358–368. doi: 10.1086/338627. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical