First demonstration of combined kV/MV image-guided real-time dynamic multileaf-collimator target tracking
- PMID: 19480969
- PMCID: PMC2720135
- DOI: 10.1016/j.ijrobp.2009.02.012
First demonstration of combined kV/MV image-guided real-time dynamic multileaf-collimator target tracking
Abstract
Purpose: For intrafraction motion management, a real-time tracking system was developed by combining fiducial marker-based tracking via simultaneous kilovoltage (kV) and megavoltage (MV) imaging and a dynamic multileaf collimator (DMLC) beam-tracking system.
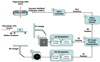
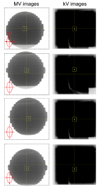
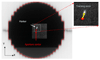
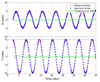
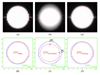
Methods and materials: The integrated tracking system employed a Varian Trilogy system equipped with kV/MV imaging systems and a Millennium 120-leaf MLC. A gold marker in elliptical motion (2-cm superior-inferior, 1-cm left-right, 10 cycles/min) was simultaneously imaged by the kV and MV imagers at 6.7 Hz and segmented in real time. With these two-dimensional projections, the tracking software triangulated the three-dimensional marker position and repositioned the MLC leaves to follow the motion. Phantom studies were performed to evaluate time delay from image acquisition to MLC adjustment, tracking error, and dosimetric impact of target motion with and without tracking.
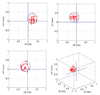
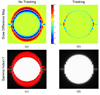
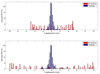
Results: The time delay of the integrated tracking system was approximately 450 ms. The tracking error using a prediction algorithm was 0.9 +/- 0.5 mm for the elliptical motion. The dose distribution with tracking showed better target coverage and less dose to surrounding region over no tracking. The failure rate of the gamma test (3%/3-mm criteria) was 22.5% without tracking but was reduced to 0.2% with tracking.
Conclusion: For the first time, a complete tracking system combining kV/MV image-guided target tracking and DMLC beam tracking was demonstrated. The average geometric error was less than 1 mm, and the dosimetric error was negligible. This system is a promising method for intrafraction motion management.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflicts of Interest Notification:
Per R. Poulsen has financial support from Varian Medical Systems, Alex Sloutsky is an employee of Varian Medical Systems and Paul J. Keall has financial support from the NIH/NCI (P01CA116602 and R01CA93626) and Varian Medical Systems.
Figures


References
-
- Grills IS, Yan D, Martinez AA, et al. Potential for reduced toxicity and dose escalation in the treatment of inoperable non-small-cell lung cancer: a comparison of intensity-modulated radiation therapy (IMRT), 3D conformal radiation, and elective nodal irradiation. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 2003;57:875–890. - PubMed
-
- Hugo G, Tenn S, Agazaryan N. An evaluation of intrafraction motion-induced error for fractionated IMRT delivery. Medical Physics. 2003;30:1470–1470.
-
- Schwarz M, Van Der Geer J, Van Herk M, et al. Impact of geometrical uncertainties on 3D CRT and IMRT dose distributions for lung cancer treatment. International Journal of Radiation Oncology Biology Physics. 2006;65:1260–1269. - PubMed
-
- Jiang SB. Radiotherapy of mobile tumors. Seminars in Radiation Oncology. 2006;16:239–248. - PubMed
-
- Keall PJ, Mageras GS, Balter JM, et al. The management of respiratory motion in radiation oncology report of AAPM Task Group 76. Med Phys. 2006;33:3874–3900. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

