14-3-3 proteins, FHA domains and BRCT domains in the DNA damage response
- PMID: 19481982
- PMCID: PMC3263375
- DOI: 10.1016/j.dnarep.2009.04.004
14-3-3 proteins, FHA domains and BRCT domains in the DNA damage response
Abstract
The DNA damage response depends on the concerted activity of protein serine/threonine kinases and modular phosphoserine/threonine-binding domains to relay the damage signal and recruit repair proteins. The PIKK family of protein kinases, which includes ATM/ATR/DNA-PK, preferentially phosphorylate Ser-Gln sites, while their basophilic downstream effecter kinases, Chk1/Chk2/MK2 preferentially phosphorylate hydrophobic-X-Arg-X-X-Ser/Thr-hydrophobic sites. A subset of tandem BRCT domains act as phosphopeptide binding modules that bind to ATM/ATR/DNA-PK substrates after DNA damage. Conversely, 14-3-3 proteins interact with substrates of Chk1/Chk2/MK2. FHA domains have been shown to interact with substrates of ATM/ATR/DNA-PK and CK2. In this review we consider how substrate phosphorylation together with BRCT domains, FHA domains and 14-3-3 proteins function to regulate ionizing radiation-induced nuclear foci and help to establish the G(2)/M checkpoint. We discuss the role of MDC1 a molecular scaffold that recruits early proteins to foci, such as NBS1 and RNF8, through distinct phosphodependent interactions. In addition, we consider the role of 14-3-3 proteins and the Chk2 FHA domain in initiating and maintaining cell cycle arrest.
Figures
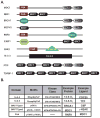
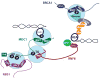
References
-
- Abraham RT. Cell cycle checkpoint signaling through the ATM and ATR kinases. Genes Dev. 2001;15:2177–2196. - PubMed
-
- Chen JS, Lin SY, Tso WL, Yeh GC, Lee WS, Tseng H, Chen LC, Ho YS. Checkpoint kinase 1-mediated phosphorylation of Cdc25C and bad proteins are involved in antitumor effects of loratadine-induced G2/M phase cell-cycle arrest and apoptosis. Mol Carcinog. 2006;45:461–478. - PubMed
-
- Manke IA, Nguyen A, Lim D, Stewart MQ, Elia AE, Yaffe MB. MAPKAP kinase-2 is a cell cycle checkpoint kinase that regulates the G2/M transition and S phase progression in response to UV irradiation. Mol Cell. 2005;17:37–48. - PubMed
-
- Li J, Taylor IA, Lloyd J, Clapperton JA, Howell S, MacMillan D, Smerdon SJ. Chk2 oligomerization studied by phosphopeptide ligation: implications for regulation and phosphodependent interactions. J Biol Chem. 2008;283:36019–36030. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

