LKB1 is required for adiponectin-mediated modulation of AMPK-S6K axis and inhibition of migration and invasion of breast cancer cells
- PMID: 19483724
- PMCID: PMC2945727
- DOI: 10.1038/onc.2009.129
LKB1 is required for adiponectin-mediated modulation of AMPK-S6K axis and inhibition of migration and invasion of breast cancer cells
Abstract
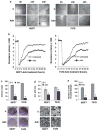
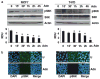
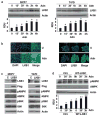
Adiponectin is widely known as an adipocytokine with therapeutic potential for its markedly protective function in the pathogenesis of obesity-related disorders, metabolic syndrome, systemic insulin resistance, cardiovascular disease and more recently carcinogenesis. In the present study, we show that adiponectin inhibits adhesion, invasion and migration of breast cancer cells. Further analysis of the underlying molecular mechanisms revealed that adiponectin treatment increased AMP-activated protein kinase (AMPK) phosphorylation and activity as evident by increased phosphorylation of downstream target of AMPK, acetyl-coenzyme A carboxylase and inhibition of p70S6 kinase (S6K). Intriguingly, we discovered that adiponectin treatment increases the expression of tumor suppressor gene LKB1 in breast cancer cells. Overexpression of LKB1 in breast cancer cells further increased adiponectin-mediated phosphorylation of AMPK. Using isogenic LKB1 knockdown cell line pair, we found that LKB1 is required for adiponectin-mediated modulation of AMPK-S6K axis and more importantly, inhibition of adhesion, migration and invasion of breast cancer cells. Taken together these data present a novel mechanism involving specific upregulation of tumor suppressor gene LKB1 by which adiponectin inhibits adhesion, invasion and migration of breast cancer cells. Our findings indicate the possibility of using adiponectin analogues to inhibit invasion and migration of breast cancer cells.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Honokiol activates AMP-activated protein kinase in breast cancer cells via an LKB1-dependent pathway and inhibits breast carcinogenesis.Breast Cancer Res. 2012 Feb 21;14(1):R35. doi: 10.1186/bcr3128. Breast Cancer Res. 2012. PMID: 22353783 Free PMC article.
-
Metastasis suppression by adiponectin: LKB1 rises up to the challenge.Cell Adh Migr. 2010 Jul-Sep;4(3):358-62. doi: 10.4161/cam.4.3.11541. Epub 2010 Jul 17. Cell Adh Migr. 2010. PMID: 20418665 Free PMC article.
-
ADIPOQ/adiponectin induces cytotoxic autophagy in breast cancer cells through STK11/LKB1-mediated activation of the AMPK-ULK1 axis.Autophagy. 2017 Aug 3;13(8):1386-1403. doi: 10.1080/15548627.2017.1332565. Epub 2017 Jul 11. Autophagy. 2017. PMID: 28696138 Free PMC article.
-
Role of the LKB1/AMPK pathway in tumor invasion and metastasis of cancer cells (Review).Oncol Rep. 2015 Dec;34(6):2821-6. doi: 10.3892/or.2015.4288. Epub 2015 Sep 18. Oncol Rep. 2015. PMID: 26398719 Review.
-
AMPKα-like proteins as LKB1 downstream targets in cell physiology and cancer.J Mol Med (Berl). 2021 May;99(5):651-662. doi: 10.1007/s00109-021-02040-y. Epub 2021 Mar 4. J Mol Med (Berl). 2021. PMID: 33661342 Review.
Cited by
-
Metabolic Syndrome and Breast Cancer: Prevalence, Treatment Response, and Prognosis.Front Oncol. 2021 Mar 25;11:629666. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2021.629666. eCollection 2021. Front Oncol. 2021. PMID: 33842335 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Integral role of PTP1B in adiponectin-mediated inhibition of oncogenic actions of leptin in breast carcinogenesis.Neoplasia. 2013 Jan;15(1):23-38. doi: 10.1593/neo.121502. Neoplasia. 2013. PMID: 23358729 Free PMC article.
-
Research progress on the correlation between obesity and the occurrence and development of kidney cancer: a narrative review.Transl Cancer Res. 2024 Oct 31;13(10):5678-5690. doi: 10.21037/tcr-24-744. Epub 2024 Oct 29. Transl Cancer Res. 2024. PMID: 39525017 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Benzyl isothiocyanate inhibits oncogenic actions of leptin in human breast cancer cells by suppressing activation of signal transducer and activator of transcription 3.Carcinogenesis. 2011 Mar;32(3):359-67. doi: 10.1093/carcin/bgq267. Epub 2010 Dec 16. Carcinogenesis. 2011. PMID: 21163886 Free PMC article.
-
Direct role of adiponectin and adiponectin receptors in endometrial cancer: in vitro and ex vivo studies in humans.Mol Cancer Ther. 2011 Dec;10(12):2234-43. doi: 10.1158/1535-7163.MCT-11-0545. Epub 2011 Oct 6. Mol Cancer Ther. 2011. PMID: 21980131 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Alessi DR, Sakamoto K, Bayascas JR. LKB1-dependent signaling pathways. Annu Rev Biochem. 2006;75:137–163. - PubMed
-
- Alimova IN, Liu B, Fan Z, Edgerton SM, Dillon T, Lind SE, et al. Metformin inhibits breast cancer cell growth, colony formation and induces cell cycle arrest in vitro. Cell Cycle. 2009;8:909–915. - PubMed
-
- Arditi JD, Venihaki M, Karalis KP, Chrousos GP. Antiproliferative effect of adiponectin on MCF7 breast cancer cells: a potential hormonal link between obesity and cancer. Horm Metab Res. 2007;39:9–13. - PubMed
-
- Barb D, Pazaitou-Panayiotou K, Mantzoros CS. Adiponectin: a link between obesity and cancer. Expert Opin Investig Drugs. 2006;15:917–931. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

