The Drosophila Pax6 paralogs have different functions in head development but can partially substitute for each other
- PMID: 19484263
- PMCID: PMC2729988
- DOI: 10.1007/s00438-009-0458-2
The Drosophila Pax6 paralogs have different functions in head development but can partially substitute for each other
Abstract
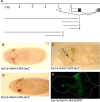
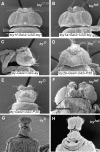
There are two Pax6 genes in Drosophila melanogaster; eyeless (ey) and twin-of-eyeless (toy), due to a duplication, which most likely occurred in the insect lineage. They encode transcription factors important for head development. Misexpression of either toy or ey can induce formation of ectopic compound eyes. Toy regulates the ey gene by binding to an eye-specific enhancer in its second intron. However, Toy can induce ectopic eyes also in an ey( - ) background, which indicates a redundancy between the two Pax6 copies in eye formation. To elucidate to what extent these two genes are interchangeable, we first generated toy-Gal4 constructs capable of driving the Pax6 genes in a toy-specific manner. Genetic dissection of the promoter proximal region of toy identified a 1,300-bp region around the canonical transcription start that is sufficient to drive toy expression in embryonic brain and eye primorida and in larval eye-antennal discs. We find that exogenous expression of toy can partially rescue the lethality and eye phenotype caused by lethal mutations in ey and vice versa. We therefore conclude that Toy and Ey, to some extent, can substitute for each other. Nevertheless, the phenotypes of the rescued flies indicate that the two Pax6 genes are specialized to regulate defined structures of the fly head.
Figures


References
-
- Bonini NM, Bui QT, Gray-Board GL, Warrick JM (1997) The Drosophila eyes absent gene directs ectopic eye formation in a pathway conserved between flies and vertebrates. Development 124:4819–4826 - PubMed
-
- Brand AH, Perrimon N (1993) Targeted gene expression as a means of altering cell fates and generating dominant phenotypes. Development 118:401–415 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

