Lipopolysaccharide alters the blood-brain barrier transport of amyloid beta protein: a mechanism for inflammation in the progression of Alzheimer's disease
- PMID: 19486646
- PMCID: PMC2783557
- DOI: 10.1016/j.bbi.2009.01.017
Lipopolysaccharide alters the blood-brain barrier transport of amyloid beta protein: a mechanism for inflammation in the progression of Alzheimer's disease
Erratum in
- Brain Behav Immun. 2011 Nov;25(8):1737. Butterfiled, D Allan [corrected to Butterfield, D Allan]
Abstract
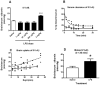
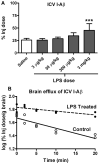
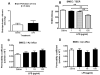
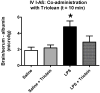
Alzheimer's disease (AD) brains are characterized by accumulation of amyloid beta protein (Abeta) and neuroinflammation. Increased blood-to-brain influx and decreased brain-to-blood efflux across the blood-brain barrier (BBB) have been proposed as mechanisms for Abeta accumulation. Epidemiological studies suggest that the nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drug (NSAID) indomethacin slows the progression of AD. We hypothesized that inflammation alters BBB handling of Abeta. Mice treated with lipopolysaccharide (LPS) had increased brain influx and decreased brain efflux of Abeta, recapitulating the findings in AD. Neither influx nor efflux was mediated by LPS acting directly on BBB cells. Increased influx was mediated by a blood-borne factor, indomethacin-independent, blocked by the triglyceride triolein, and not related to expression of the blood-to-brain transporter of Abeta, RAGE. Serum levels of IL-6, IL-10, IL-13, and MCP-1 mirrored changes in Abeta influx. Decreased efflux was blocked by indomethacin and accompanied by decreased protein expression of the brain-to-blood transporter of Abeta, LRP-1. LPS paradoxically increased expression of neuronal LRP-1, a major source of Abeta. Thus, inflammation potentially increases brain levels of Abeta by three mechanisms: increased influx, decreased efflux, and increased neuronal production.
Figures

References
-
- Banks WA, Clever CM, Farrell CL. Partial saturation and regional variation in the blood to brain transport of leptin in normal weight mice. Am J Physiol. 2000;278:E1158–E1165. - PubMed
-
- Banks WA, Coon AB, Robinson SM, Moinuddin A, Shultz JM, Nakaoke R, Morley JE. Triglycerides induce leptin resistance at the blood-brain barrier. Diabetes. 2004;53:1253–1260. - PubMed
-
- Banks WA, Fasold MB, Kastin AJ. Measurement of efflux rate from brain to blood. In: Irvine GB, Williams CH, editors. Methods in Molecular Biology: Neuropeptides Protocols. Humana Press; Totowa, NJ: 1997. pp. 353–360. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

