Overall survival and updated results for sunitinib compared with interferon alfa in patients with metastatic renal cell carcinoma
- PMID: 19487381
- PMCID: PMC3646307
- DOI: 10.1200/JCO.2008.20.1293
Overall survival and updated results for sunitinib compared with interferon alfa in patients with metastatic renal cell carcinoma
Abstract
Purpose: A randomized, phase III trial demonstrated superiority of sunitinib over interferon alfa (IFN-alpha) in progression-free survival (primary end point) as first-line treatment for metastatic renal cell carcinoma (RCC). Final survival analyses and updated results are reported.
Patients and methods: Seven hundred fifty treatment-naïve patients with metastatic clear cell RCC were randomly assigned to sunitinib 50 mg orally once daily on a 4 weeks on, 2 weeks off dosing schedule or to IFN-alpha 9 MU subcutaneously thrice weekly. Overall survival was compared by two-sided log-rank and Wilcoxon tests. Progression-free survival, response, and safety end points were assessed with updated follow-up.
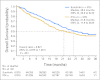
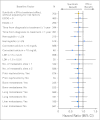
Results: Median overall survival was greater in the sunitinib group than in the IFN-alpha group (26.4 v 21.8 months, respectively; hazard ratio [HR] = 0.821; 95% CI, 0.673 to 1.001; P = .051) per the primary analysis of unstratified log-rank test (P = .013 per unstratified Wilcoxon test). By stratified log-rank test, the HR was 0.818 (95% CI, 0.669 to 0.999; P = .049). Within the IFN-alpha group, 33% of patients received sunitinib, and 32% received other vascular endothelial growth factor-signaling inhibitors after discontinuation from the trial. Median progression-free survival was 11 months for sunitinib compared with 5 months for IFN-alpha (P < .001). Objective response rate was 47% for sunitinib compared with 12% for IFN-alpha (P < .001). The most commonly reported sunitinib-related grade 3 adverse events included hypertension (12%), fatigue (11%), diarrhea (9%), and hand-foot syndrome (9%).
Conclusion: Sunitinib demonstrates longer overall survival compared with IFN-alpha plus improvement in response and progression-free survival in the first-line treatment of patients with metastatic RCC. The overall survival highlights an improved prognosis in patients with RCC in the era of targeted therapy.
Conflict of interest statement
Authors' disclosures of potential conflicts of interest and author contributions are found at the end of this article.
Figures

Republished in
-
Overall Survival and Updated Results for Sunitinib Compared With Interferon Alfa in Patients With Metastatic Renal Cell Carcinoma.J Clin Oncol. 2023 Apr 10;41(11):1965-1971. doi: 10.1200/JCO.22.02623. J Clin Oncol. 2023. PMID: 37018919 Clinical Trial.
Comment in
-
Effective therapy for metastatic renal cancer, whither to now.J Clin Oncol. 2009 Aug 1;27(22):3573-4. doi: 10.1200/JCO.2009.22.5250. Epub 2009 Jun 1. J Clin Oncol. 2009. PMID: 19487371 No abstract available.
-
Targeted therapies: Sunitinib versus interferon-alpha in metastatic RCC.Nat Rev Clin Oncol. 2010 Jan;7(1):7-8. doi: 10.1038/nrclinonc.2009.173. Nat Rev Clin Oncol. 2010. PMID: 20029441
References
-
- Chow LQ, Eckhardt SG. Sunitinib: From rational design to clinical efficacy. J Clin Oncol. 2007;25:884–896. - PubMed
-
- Motzer RJ, Rini BI, Bukowski RM, et al. Sunitinib in patients with metastatic renal cell carcinoma. JAMA. 2006;295:2516–2524. - PubMed
-
- Motzer RJ, Michaelson MD, Rosenberg J, et al. Sunitinib efficacy against advanced renal cell carcinoma. J Urol. 2007;178:1883–1887. - PubMed
-
- Motzer RJ, Hutson TE, Tomczak P, et al. Sunitinib versus interferon alfa in metastatic renal-cell carcinoma. N Engl J Med. 2007;356:115–124. - PubMed
-
- Therasse P, Arbuck SG, Eisenhauer EA, et al. New guidelines to evaluate the response to treatment in solid tumors. J Natl Cancer Inst. 2000;92:205–216. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials

