A Drosophila resource of transgenic RNAi lines for neurogenetics
- PMID: 19487563
- PMCID: PMC2728850
- DOI: 10.1534/genetics.109.103630
A Drosophila resource of transgenic RNAi lines for neurogenetics
Abstract
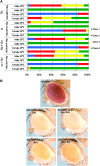
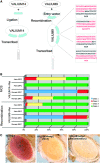
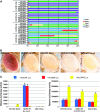
Conditional expression of hairpin constructs in Drosophila is a powerful method to disrupt the activity of single genes with a spatial and temporal resolution that is impossible, or exceedingly difficult, using classical genetic methods. We previously described a method (Ni et al. 2008) whereby RNAi constructs are targeted into the genome by the phiC31-mediated integration approach using Vermilion-AttB-Loxp-Intron-UAS-MCS (VALIUM), a vector that contains vermilion as a selectable marker, an attB sequence to allow for phiC31-targeted integration at genomic attP landing sites, two pentamers of UAS, the hsp70 core promoter, a multiple cloning site, and two introns. As the level of gene activity knockdown associated with transgenic RNAi depends on the level of expression of the hairpin constructs, we generated a number of derivatives of our initial vector, called the "VALIUM" series, to improve the efficiency of the method. Here, we report the results from the systematic analysis of these derivatives and characterize VALIUM10 as the most optimal vector of this series. A critical feature of VALIUM10 is the presence of gypsy insulator sequences that boost dramatically the level of knockdown. We document the efficacy of VALIUM as a vector to analyze the phenotype of genes expressed in the nervous system and have generated a library of 2282 constructs targeting 2043 genes that will be particularly useful for studies of the nervous system as they target, in particular, transcription factors, ion channels, and transporters.
Figures



References
-
- Achara, J. K., K. Jalink, R. W. Hardy, V. Hartenstein and C. S. Zuker, 1997. InsP3 receptor is essential for growth and differentiation but not for vision in Drosophila. Neuron 18 881–887. - PubMed
-
- Barolo, S., L. A. Carver and J. W. Posakony, 2000. GFP and beta-galactosidase transformation vectors for promoter/enhancer analysis in Drosophila. Biotechniques 29 726–732. - PubMed
-
- Brand, A. H., and N. Perrimon, 1993. Targeted gene expression as a means of altering cell fates and generating dominant phenotypes. Development 118 401–415. - PubMed
-
- Dietzl, G., D. Chen, F. Schnorrer, K. C. Su, Y. Barinova et al., 2007. A genome-wide transgenic RNAi library for conditional gene inactivation in Drosophila. Nature 448 151–156. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

