Circulating fibroblast growth factor-21 is elevated in impaired glucose tolerance and type 2 diabetes and correlates with muscle and hepatic insulin resistance
- PMID: 19487637
- PMCID: PMC2713625
- DOI: 10.2337/dc09-0684
Circulating fibroblast growth factor-21 is elevated in impaired glucose tolerance and type 2 diabetes and correlates with muscle and hepatic insulin resistance
Abstract
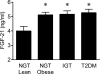
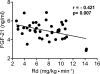
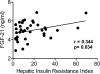
OBJECTIVE Fibroblast growth factor (FGF)-21 is highly expressed in the liver and regulates hepatic glucose production and lipid metabolism in rodents. However, its role in the pathogenesis of type 2 diabetes in humans remains to be defined. The aim of this study was to quantitate circulating plasma FGF-21 levels and examine their relationship with insulin sensitivity in subjects with varying degrees of obesity and glucose tolerance. RESEARCH DESIGN AND METHODS Forty-one subjects (8 lean with normal glucose tolerance [NGT], 9 obese with NGT, 12 with impaired fasting glucose [IFG]/impaired glucose tolerance [IGT], and 12 type 2 diabetic subjects) received an oral glucose tolerance test (OGTT) and a hyperinsulinemic-euglycemic clamp (80 mU/m(2) per min) combined with 3-[(3)H] glucose infusion. RESULTS Subjects with type 2 diabetes, subjects with IGT, and obese subjects with NGT were insulin resistant compared with lean subjects with NGT. Plasma FGF-21 levels progressively increased from 3.9 +/- 0.3 ng/ml in lean subjects with NGT to 4.9 +/- 0.2 in obese subjects with NGT to 5.2 +/- 0.2 in subjects with IGT and to 5.3 +/- 0.2 in type 2 diabetic subjects. FGF-21 levels correlated inversely with whole-body (primarily reflects muscle) insulin sensitivity (r = -0.421, P = 0.007) and directly with the hepatic insulin resistance index (r = 0.344, P = 0.034). FGF-21 levels also correlated with measures of glycemia (fasting plasma glucose [r = 0.312, P = 0.05], 2-h plasma glucose [r = 0.414, P = 0.01], and A1C [r = 0.325, P = 0.04]). CONCLUSIONS Plasma FGF-21 levels are increased in insulin-resistant states and correlate with hepatic and whole-body (muscle) insulin resistance. FGF-21 may play a role in pathogenesis of hepatic and whole-body insulin resistance in type 2 diabetes.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Retinol-binding protein 4 is associated with impaired glucose tolerance but not with whole body or hepatic insulin resistance in Mexican Americans.Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab. 2009 Apr;296(4):E758-64. doi: 10.1152/ajpendo.90737.2008. Epub 2009 Feb 3. Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab. 2009. PMID: 19190263
-
Impaired early- but not late-phase insulin secretion in subjects with impaired fasting glucose.Acta Diabetol. 2011 Sep;48(3):209-17. doi: 10.1007/s00592-011-0285-x. Epub 2011 May 8. Acta Diabetol. 2011. PMID: 21553243 Clinical Trial.
-
Relationship between hepatic/visceral fat and hepatic insulin resistance in nondiabetic and type 2 diabetic subjects.Gastroenterology. 2007 Aug;133(2):496-506. doi: 10.1053/j.gastro.2007.04.068. Epub 2007 May 1. Gastroenterology. 2007. PMID: 17681171
-
Measuring and estimating insulin resistance in clinical and research settings.Obesity (Silver Spring). 2022 Aug;30(8):1549-1563. doi: 10.1002/oby.23503. Obesity (Silver Spring). 2022. PMID: 35894085 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Skeletal muscle insulin resistance is the primary defect in type 2 diabetes.Diabetes Care. 2009 Nov;32 Suppl 2(Suppl 2):S157-63. doi: 10.2337/dc09-S302. Diabetes Care. 2009. PMID: 19875544 Free PMC article. Review. No abstract available.
Cited by
-
Endocrine fibroblast growth factors 15/19 and 21: from feast to famine.Genes Dev. 2012 Feb 15;26(4):312-24. doi: 10.1101/gad.184788.111. Epub 2012 Feb 2. Genes Dev. 2012. PMID: 22302876 Free PMC article. Review.
-
High glucose represses β-klotho expression and impairs fibroblast growth factor 21 action in mouse pancreatic islets: involvement of peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor γ signaling.Diabetes. 2013 Nov;62(11):3751-9. doi: 10.2337/db13-0645. Epub 2013 Jul 29. Diabetes. 2013. PMID: 23897951 Free PMC article.
-
Mistranslation Drives Alterations in Protein Levels and the Effects of a Synonymous Variant at the Fibroblast Growth Factor 21 Locus.Adv Sci (Weinh). 2021 May 1;8(11):2004168. doi: 10.1002/advs.202004168. eCollection 2021 Jun. Adv Sci (Weinh). 2021. PMID: 34141520 Free PMC article.
-
Independent Association of Serum Fibroblast Growth Factor 21 Levels With Impaired Liver Enzymes in Hyperthyroid Patients.Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2019 Jan 14;9:800. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2018.00800. eCollection 2018. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2019. PMID: 30692965 Free PMC article.
-
Metabolic Stress Index Including Mitochondrial Biomarker for Noninvasive Diagnosis of Hepatic Steatosis.Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2022 May 19;13:896334. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2022.896334. eCollection 2022. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2022. PMID: 35663311 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Bottcher RT, Niehrs C: Fibroblast growth factor signaling during early vertebrate development. Endocr Rev 2005; 26: 63– 77 - PubMed
-
- Huang X, Yu C, Jin C, Yang C, Xie R, Cao D, Wang F, McKeehan WL: Forced expression of hepatocyte-specific fibroblast growth factor 21 delays initiation of chemically induced hepatocarcinogenesis. Mol Carcinog 2006; 45: 934– 942 - PubMed
-
- Goetz R, Beenken A, Ibrahimi OA, Kalinina J, Olsen SK, Eliseenkova AV, Xu C, Neubert TA, Zhang F, Linhardt RJ, Yu X, White KE, Inagaki T, Kliewer SA, Yamamoto M, Kurosu H, Ogawa Y, Kuro-o M, Lanske B, Razzaque MS, Mohammadi M: Molecular insights into the klotho-dependent, endocrine mode of action of fibroblast growth factor 19 subfamily members. Mol Cell Biol 2007; 27: 3417– 3428 - PMC - PubMed
-
- Kharitonenkov A, Wroblewski VJ, Koester A, Chen YF, Clutinger CK, Tigno XT, Hansen BC, Shanafelt AB, Etgen GJ: The metabolic state of diabetic monkeys is regulated by fibroblast growth factor-21. Endocrinology 2007; 148: 774– 781 - PubMed
-
- Fu L, John LM, Adams SH, Yu XX, Tomlinson E, Renz M, Williams PM, Soriano R, Corpuz R, Moffat B, Vandlen R, Simmons L, Foster J, Stephan JP, Tsai SP, Stewart TA: Fibroblast growth factor 19 increases metabolic rate and reverses dietary and leptin-deficient diabetes. Endocrinology 2004; 145: 2594– 2603 - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials

