Incident dysglycemia and progression to type 1 diabetes among participants in the Diabetes Prevention Trial-Type 1
- PMID: 19487644
- PMCID: PMC2732147
- DOI: 10.2337/dc08-2140
Incident dysglycemia and progression to type 1 diabetes among participants in the Diabetes Prevention Trial-Type 1
Abstract
Objective: We studied the incidence of dysglycemia and its prediction of the development of type 1 diabetes in islet cell autoantibody (ICA)-positive individuals. In addition, we assessed whether dysglycemia was sustained.
Research design and methods: Participants (n = 515) in the Diabetes Prevention Trial-Type 1 (DPT-1) with normal glucose tolerance who underwent periodic oral glucose tolerance tests (OGTTs) were followed for incident dysglycemia (impaired fasting glucose, impaired glucose tolerance, and/or high glucose levels at intermediate time points of OGTTs). Incident dysglycemia at the 6-month visit was assessed for type 1 diabetes prediction.
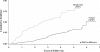
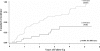
Results: Of 515 participants with a normal baseline OGTT, 310 (60%) had at least one episode of dysglycemia over a maximum follow-up of 7 years. Dysglycemia at the 6-month visit was highly predictive of the development of type 1 diabetes, both in those aged <13 years (P < 0.001) and those aged > or =13 years (P < 0.01). Those aged <13 years with dysglycemia at the 6-month visit had a high cumulative incidence (94% estimate by 5 years). Among those who developed type 1 diabetes after a dysglycemic OGTT and who had at least two OGTTs after the dysglycemic OGTT, 33 of 64 (52%) reverted back to a normal OGTT. However, 26 (79%) of the 33 then had another dysglycemic OGTT before diagnosis.
Conclusions: ICA-positive individuals with normal glucose tolerance had a high incidence of dysglycemia. Incident dysglycemia in those who are ICA positive is strongly predictive of type 1 diabetes. Children with incident dysglycemia have an especially high risk. Fluctuations in and out of the dysglycemic state are not uncommon before the onset of type 1 diabetes.
Figures
References
-
- Rosenbloom AL, Hunt SS, Rosenbloom EK, Maclaren NK: Ten-year prognosis of impaired glucose tolerance in siblings of patients with insulin-dependent diabetes. Diabetes 1982; 31: 385– 387 - PubMed
-
- Beer SF, Heaton DA, Alberti KGMM, Pyke A, Leslie RDG: Impaired glucose tolerance precedes but does not predict insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus: a study of identical twins. Diabetologia 1990; 33: 497– 502 - PubMed
-
- Sosenko J, Palmer JP, Greenbaum CJ, Mahon J, Cowie C, Krischer JP, Chase HP, White NH, Buckingham B, Herold KC, Cuthbertson D, Skyler JS: Diabetes Prevention Trial-Type 1 Study Group. Patterns of metabolic progression to type 1 diabetes in the diabetes prevention trial-type 1. Diabetes Care 2006; 29: 643– 649 - PubMed
-
- Diabetes Prevention Trial-Type 1 Diabetes Study Group Effects of insulin in relatives of patients with type 1 diabetes mellitus. N Engl J Med 2002; 346: 1685– 1691 - PubMed
-
- Diabetes Prevention Trial-Type 1 Diabetes Study Group Effects of oral insulin in relatives of patients with type 1 diabetes. Diabetes Care 2005; 28: 1068– 1076 - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

