Proximity of excitatory and inhibitory axon terminals adjacent to pyramidal cell bodies provides a putative basis for nonsynaptic interactions
- PMID: 19487685
- PMCID: PMC2701041
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.0900330106
Proximity of excitatory and inhibitory axon terminals adjacent to pyramidal cell bodies provides a putative basis for nonsynaptic interactions
Abstract
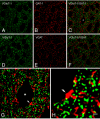
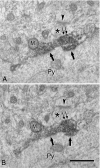
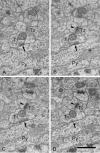
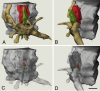
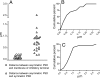
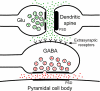
Although pyramidal cells are the main excitatory neurons in the cerebral cortex, it has recently been reported that they can evoke inhibitory postsynaptic currents in neighboring pyramidal neurons. These inhibitory effects were proposed to be mediated by putative axo-axonic excitatory synapses between the axon terminals of pyramidal cells and perisomatic inhibitory axon terminals [Ren M, Yoshimura Y, Takada N, Horibe S, Komatsu Y (2007) Science 316:758-761]. However, the existence of this type of axo-axonic synapse was not found using serial section electron microscopy. Instead, we observed that inhibitory axon terminals synapsing on pyramidal cell bodies were frequently apposed by terminals that established excitatory synapses with neighbouring dendrites. We propose that a spillover of glutamate from these excitatory synapses can activate the adjacent inhibitory axo-somatic terminals.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- DeFelipe J, Jones EG. Cajal on the Cerebral Cortex. New York: Oxford Univ Press; 1988.
-
- DeFelipe J, Fariñas I. The pyramidal neuron of the cerebral cortex: Morphological and chemical characteristics of the synaptic inputs. Prog Neurobiol. 1992;39:563–607. - PubMed
-
- Spruston N. Pyramidal neurons: Dendritic structure and synaptic integration. Nat Rev Neurosci. 2008;9:206–221. - PubMed
-
- Ren M, Yoshimura Y, Takada N, Horibe S, Komatsu Y. Specialized inhibitory synaptic actions between nearby neocortical pyramidal neurons. Science. 2007;316:758–761. - PubMed
-
- Ribak CE. Aspinous and sparsely-spinous stellate neurons in the visual cortex of rats contain glutamic acid decarboxylase. J Neurocytol. 1978;7:461–478. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

