Signals, regulatory networks, and materials that build and break bacterial biofilms
- PMID: 19487730
- PMCID: PMC2698413
- DOI: 10.1128/MMBR.00041-08
Signals, regulatory networks, and materials that build and break bacterial biofilms
Abstract
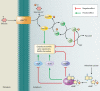
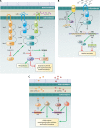
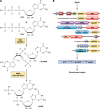
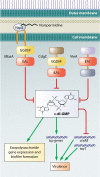
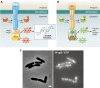
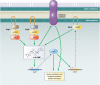
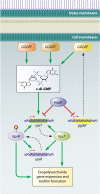
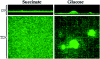
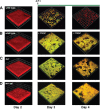
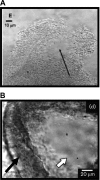
Biofilms are communities of microorganisms that live attached to surfaces. Biofilm formation has received much attention in the last decade, as it has become clear that virtually all types of bacteria can form biofilms and that this may be the preferred mode of bacterial existence in nature. Our current understanding of biofilm formation is based on numerous studies of myriad bacterial species. Here, we review a portion of this large body of work including the environmental signals and signaling pathways that regulate biofilm formation, the components of the biofilm matrix, and the mechanisms and regulation of biofilm dispersal.
Figures
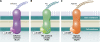

References
-
- Aldridge, P., and U. Jenal. 1999. Cell cycle-dependent degradation of a flagellar motor component requires a novel-type response regulator. Mol. Microbiol. 32379-391. - PubMed
-
- Allesen-Holm, M., K. B. Barken, L. Yang, M. Klausen, J. S. Webb, S. Kjelleberg, S. Molin, M. Givskov, and T. Tolker-Nielsen. 2006. A characterization of DNA release in Pseudomonas aeruginosa cultures and biofilms. Mol. Microbiol. 591114-1128. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

