Correlations between plasma levels of a fibronectin isoform subpopulation and C-reactive protein in patients with systemic inflammatory disease
- PMID: 19489687
- PMCID: PMC2746117
- DOI: 10.1080/13547500902836032
Correlations between plasma levels of a fibronectin isoform subpopulation and C-reactive protein in patients with systemic inflammatory disease
Abstract
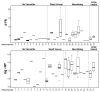
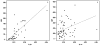
Surrogate markers to detect vasculitic processes prior to organ compromise are lacking. To determine if specific populations among the fibronectin (FN) family of alternatively spliced proteins correlate with parameters of vasculitis in at-risk patients, we retrospectively evaluated the association of plasma levels of total FN (TFN) and FN bearing the alternatively spliced EIIIA segment (A(+)FN) with clinical vasculitis status and with levels of two putative vasculitis markers (C-reactive protein (CRP) and von Willebrand factor) in a previously studied cohort of 27 patients with systemic inflammatory disease. We found that the percentage of TFN composed by A(+)FN (%A(+)) and A(+)FN, but not TFN, correlated with plasma levels of CRP, the prototypic inflammation biomarker used to detect vasculitis. These findings suggest that different FNs may confer distinct clinical information, and that their simultaneous measurement merits further investigation in our efforts to identify soluble biomarker systems to detect vasculitis.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Plasma levels of fibronectin bearing the alternatively spliced EIIIB segment are increased after major trauma.J Lab Clin Med. 2003 Jun;141(6):401-10. doi: 10.1016/S0022-2143(03)00042-8. J Lab Clin Med. 2003. PMID: 12819638
-
The role of antineutrophil cytoplasm antibodies, anticardiolipin antibodies, von Willebrand factor antigen, and fibronectin for the diagnosis of systemic vasculitis.J Rheumatol. 1991 Aug;18(8):1199-206. J Rheumatol. 1991. PMID: 1941824
-
Increased Ed-B fibronectin plasma levels in spondyloarthropathies: comparison with rheumatoid arthritis patients and a healthy population.Rheumatology (Oxford). 1999 Nov;38(11):1099-103. doi: 10.1093/rheumatology/38.11.1099. Rheumatology (Oxford). 1999. PMID: 10556262
-
Fibronectin and its soluble EDA-FN isoform as biomarkers for inflammation and sepsis.Adv Clin Exp Med. 2019 Nov;28(11):1561-1567. doi: 10.17219/acem/104531. Adv Clin Exp Med. 2019. PMID: 31596557 Review.
-
Assessment of disease activity in systemic vasculitis.Postgrad Med J. 1998 Jan;74(867):1-6. doi: 10.1136/pgmj.74.867.1. Postgrad Med J. 1998. PMID: 9538478 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Changes in plasma fibronectin isoform levels predict distinct clinical outcomes in critically ill patients.Biomark Insights. 2011;6:59-68. doi: 10.4137/BMI.S7204. Epub 2011 May 29. Biomark Insights. 2011. PMID: 21695089 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Blake GJ, Ridker PM. C-reactive protein: a surrogate risk marker or mediator of atherothrombosis? Am J Physiol Regul Integr Comp Physiol. 2003;285:R1250–1252. - PubMed
-
- Castellanos M, Leira R, Serena J, Blanco M, Pedraza S, Castillo J, Davalos A. Plasma cellular-fibronectin concentration predicts hemorrhagic transformation after thrombolytic therapy in acute ischemic stroke. Stroke. 2004;35:1671–1676. - PubMed
-
- Dubin D, Peters JH, Brown LF, Logan B, Kent KC, Berse B, Berven S, Cercek B, Sharifi BG, Pratt RE, et al. Balloon catheterization induced arterial expression of embryonic fibronectins. Arteriosclerosis, Thrombosis, and Vascular Biology. 1995;15:1958–1967. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
