Cip/Kip cyclin-dependent protein kinase inhibitors and the road to polyploidy
- PMID: 19490616
- PMCID: PMC2697143
- DOI: 10.1186/1747-1028-4-10
Cip/Kip cyclin-dependent protein kinase inhibitors and the road to polyploidy
Abstract
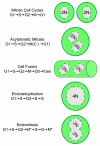
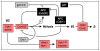
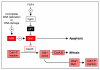
Cyclin-dependent kinases (CDKs) play a central role in the orderly transition from one phase of the eukaryotic mitotic cell division cycle to the next. In this context, p27Kip1 (one of the CIP/KIP family of CDK specific inhibitors in mammals) or its functional analogue in other eukarya prevents a premature transition from G1 to S-phase. Recent studies have revealed that expression of a second member of this family, p57Kip2, is induced as trophoblast stem (TS) cells differentiate into trophoblast giant (TG) cells. p57 then inhibits CDK1 activity, an enzyme essential for initiating mitosis, thereby triggering genome endoreduplication (multiple S-phases without an intervening mitosis). Expression of p21Cip1, the third member of this family, is also induced in during differentiation of TS cells into TG cells where it appears to play a role in suppressing the DNA damage response pathway. Given the fact that p21 and p57 are unique to mammals, the question arises as to whether one or both of these proteins are responsible for the induction and maintenance of polyploidy during mammalian development.
Figures
References
-
- Saxena S, Dutta A. Geminin-Cdt1 balance is critical for genetic stability. Mutat Res. 2005;569:111–121. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

