The effect of Lipoxin A4 on the interaction between macrophage and osteoblast: possible role in the treatment of aseptic loosening
- PMID: 19490628
- PMCID: PMC2698870
- DOI: 10.1186/1471-2474-10-57
The effect of Lipoxin A4 on the interaction between macrophage and osteoblast: possible role in the treatment of aseptic loosening
Abstract
Background: Aseptic loosening (AL) is the main problem of total joints replacement (TJR) by the implantation of permanently prosthetic components. In vitro and in vivo studies have clearly demonstrated that wear debris and its byproducts could trigger inflammation in the peri-implant tissue. Lipoxins (LXs) are endogenous eicosanoids synthesized locally from arachidonate acid (AA) at sites of inflammation and mediate pro-resolving activity. A number of studies have demonstrated the effect of LXA4 to counteract inflammation in different cell and animal models, but till now, no relative report about the role of LXs in progress or prevention of AL.
Methods: Murine RAW264.7 macrophage cell line and MC3T3-E1 osteoblasts (OB) cell line were purchased. Co-cultured model of these two cell lines was established. To explore the effect of exogenous Lipoxin A4 (LXA4) on polymethylmethacrylate (PMMA) induced inflammation, pro-inflammatory cytokines including TNF-alpha, IL-1beta, PGE2 and GM-CSF were measured by ELISA kits and bone resorption was quantified by measuring calcium release from 5-day-old mice calvaria in vitro. To determine further the endogenous effect of LXA4, cells were co-cultured and with or without 15-lipoxygease (15-LO) blocking by 15-LO siRNA. Both real-time PCR and western blotting were applied to confirm the inhibitory efficiency of 15-LO by siRNA.
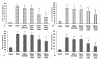
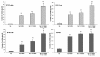
Results: 0.1 mg/ml, 0.5 mg/ml and 1.0 mg/ml PMMA showed a time-dependent manner to trigger production of all the pro-inflammatory cytokines studied. Exogenous 0-100 nM LXA4 presented an inhibitory effect on both generation of above cytokines and PMMA stimulated calvarial bone resorption with a dose-dependent manner. LXA4 in supernatant from neither rest macrophages nor macrophages cultured alone exposing to PMMA was detectable. In co-cultured cells challenged by PMMA, LXA4 was increased significantly, while, this enhance could be partly inhibited by 15-LO siRNA. When LXA4 generation was blocked with 15-LO siRNA, the PMMA induced pro-inflammatory cytokines were elevated and bone resorption was accelerated.
Conclusion: In the present study, we demonstrated that LXA4 had a favorable inhibitory effect on PMMA-induced inflammation in a macrophage and OB co-culture system.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Lipoxin A(4) reduces lipopolysaccharide-induced inflammation in macrophages and intestinal epithelial cells through inhibition of nuclear factor-kappaB activation.J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 2010 Feb;332(2):541-8. doi: 10.1124/jpet.109.159046. Epub 2009 Oct 21. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 2010. PMID: 19846590
-
Lipoxins Protect Against Inflammation in Diabetes-Associated Atherosclerosis.Diabetes. 2018 Dec;67(12):2657-2667. doi: 10.2337/db17-1317. Epub 2018 Sep 13. Diabetes. 2018. PMID: 30213823
-
Lipoxins and aspirin-triggered lipoxin alleviate bone cancer pain in association with suppressing expression of spinal proinflammatory cytokines.J Neuroinflammation. 2012 Dec 26;9:278. doi: 10.1186/1742-2094-9-278. J Neuroinflammation. 2012. PMID: 23268791 Free PMC article.
-
Lipoxins and aspirin-triggered 15-epi-lipoxins are the first lipid mediators of endogenous anti-inflammation and resolution.Prostaglandins Leukot Essent Fatty Acids. 2005 Sep-Oct;73(3-4):141-62. doi: 10.1016/j.plefa.2005.05.002. Prostaglandins Leukot Essent Fatty Acids. 2005. PMID: 16005201 Review.
-
Lipoxin and synthetic lipoxin analogs: an overview of anti-inflammatory functions and new concepts in immunomodulation.Inflamm Allergy Drug Targets. 2006 Apr;5(2):91-106. doi: 10.2174/187152806776383125. Inflamm Allergy Drug Targets. 2006. PMID: 16613568 Review.
Cited by
-
Effects of ω3- and ω6-polyunsaturated fatty acids on RANKL-induced osteoclast differentiation of RAW264.7 cells: a comparative in vitro study.Nutrients. 2014 Jul 9;6(7):2584-601. doi: 10.3390/nu6072584. Nutrients. 2014. PMID: 25010555 Free PMC article.
-
The Effects of Biomaterial Implant Wear Debris on Osteoblasts.Front Cell Dev Biol. 2020 Jun 3;8:352. doi: 10.3389/fcell.2020.00352. eCollection 2020. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2020. PMID: 32582688 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The role of polyunsaturated ω-3 fatty acid eicosapentaenoic acid-derived resolvin E1 (RvE1) in bone preservation.Crit Rev Immunol. 2014;34(4):347-57. doi: 10.1615/critrevimmunol.2014009982. Crit Rev Immunol. 2014. PMID: 24941160 Free PMC article. Review.
-
CORR Insights®: What Host Factors Affect Aseptic Loosening After THA and TKA?Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2015 Aug;473(8):2710-1. doi: 10.1007/s11999-015-4251-8. Epub 2015 Mar 14. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2015. PMID: 25773904 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
What Host Factors Affect Aseptic Loosening After THA and TKA?Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2015 Aug;473(8):2700-9. doi: 10.1007/s11999-015-4220-2. Epub 2015 Feb 26. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2015. PMID: 25716213 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Kokoszka P, Staszczuk P, Redman M, Pislewski Z, Pietrzak K. [Evaluation of outcomes following total hip arthroplasty] Chir Narzadow Ruchu Ortop Pol. 2008;73:94–100. - PubMed
-
- Ren W, Markel DC, Schwendener R, Ding Y, Wu B, Wooley PH. Macrophage depletion diminishes implant-wear-induced inflammatory osteolysis in a mouse model. J Biomed Mater Res A. 2008;85:1043–1051. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

