Leptin-dependent control of glucose balance and locomotor activity by POMC neurons
- PMID: 19490908
- PMCID: PMC2730605
- DOI: 10.1016/j.cmet.2009.05.003
Leptin-dependent control of glucose balance and locomotor activity by POMC neurons
Abstract
Leptin plays a pivotal role in regulation of energy balance. Via unknown central pathways, leptin also affects peripheral glucose homeostasis and locomotor activity. We hypothesized that, specifically, pro-opiomelanocortin (POMC) neurons mediate those actions. To examine this possibility, we applied Cre-Lox technology to express leptin receptors (ObRb) exclusively in POMC neurons of the morbidly obese, profoundly diabetic, and severely hypoactive leptin receptor-deficient Lepr(db/db) mice. Here, we show that expression of ObRb only in POMC neurons leads to a marked decrease in energy intake and a modest reduction in body weight in Lepr(db/db) mice. Remarkably, blood glucose levels are entirely normalized. This normalization occurs independently of changes in food intake and body weight. In addition, physical activity is greatly increased despite profound obesity. Our results suggest that leptin signaling exclusively in POMC neurons is sufficient to stimulate locomotion and prevent diabetes in the severely hypoactive and hyperglycemic obese Lepr(db/db) mice.
Figures
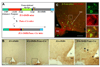
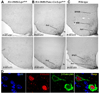

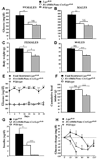

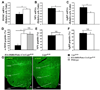
References
-
- Baetens D, Stefan Y, Ravazzola M, Malaisse-Lagae F, Coleman DL, Orci L. Alteration of islet cell populations in spontaneously diabetic mice. Diabetes. 1978;27:1–7. - PubMed
-
- Balthasar N, Coppari R, McMinn J, Liu SM, Lee CE, Tang V, Kenny CD, McGovern RA, Chua SC, Jr, Elmquist JK, Lowell BB. Leptin receptor signaling in POMC neurons is required for normal body weight homeostasis. Neuron. 2004;42:983–991. - PubMed
-
- Brito MN, Brito NA, Baro DJ, Song CK, Bartness TJ. Differential activation of the sympathetic innervation of adipose tissues by melanocortin receptor stimulation. Endocrinology. 2007;148:5339–5347. - PubMed
-
- Chen H, Charlat O, Tartaglia LA, Woolf EA, Weng X, Ellis SJ, Lakey ND, Culpepper J, Moore KJ, Breitbart RE. Evidence that the diabetes gene encodes the leptin receptor: identification of a mutation in the leptin receptor gene in db/db mice. Cell. 1996;84:491–495. - PubMed
-
- Coleman DL. Obese and diabetes: two mutant genes causing diabetes-obesity syndromes in mice. Diabetologia. 1978;14:141–148. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

