A cembranoid from tobacco prevents the expression of nicotine-induced withdrawal behavior in planarian worms
- PMID: 19490913
- PMCID: PMC2904570
- DOI: 10.1016/j.ejphar.2009.05.022
A cembranoid from tobacco prevents the expression of nicotine-induced withdrawal behavior in planarian worms
Abstract
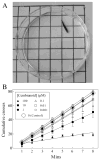
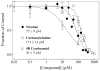
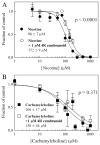
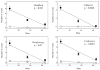
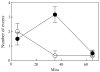
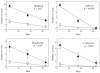
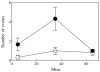
Using an adaptation of published behavioral protocols, we determined that acute exposure to the cholinergic compounds nicotine and carbamylcholine decreased planarian motility in a concentration-dependent manner. A tobacco cembranoid (1S,2E,4R,6R,7E,11E)-cembra-2,7,11-triene-4,6-diol (4R-cembranoid), also decreased planarian motility. Experiments in the presence of 1 microM 4R-cembranoid did increase the IC50 for nicotine- but not carbamylcholine-induced decrease in planarian motility. When planarians were exposed for 24 h to either nicotine or carbamylcholine at concentrations near their respective IC50 values and then transferred to plain media, nicotine-exposed, but not carbamylcholine- or cembranoid-exposed worms displayed withdrawal-like distress behaviors. In experiments where planarians were pre-exposed to 100 microM nicotine for 24 h in the presence of 1 microM 4R-cembranoid, the withdrawal-like effects were significantly reduced. These results indicate that the 4R-cembranoid might have valuable applications for tobacco abuse research. This experimental approach using planarians is useful for the initial screening of compounds relevant to drug abuse and dependence.
Conflict of interest statement
V.A.E. and O.R.P. are co-discoverers on two cembranoid-related patents: US 6,204,289.
B1 — “Cembranoid Inhibitors of Nicotinic Acetylcholine Receptors” and US 6,489,357 B1 — “Tobacco Cembranoids Block the Expression of Behavioral Sensitization to Nicotine and Inhibit Neuronal Acetylcholine Receptors”.
Figures
Similar articles
-
A Review on Bioactivities of Tobacco Cembranoid Diterpenes.Biomolecules. 2019 Jan 16;9(1):30. doi: 10.3390/biom9010030. Biomolecules. 2019. PMID: 30654586 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Parthenolide prevents the expression of cocaine-induced withdrawal behavior in planarians.Eur J Pharmacol. 2008 Mar 31;583(1):170-2. doi: 10.1016/j.ejphar.2008.01.012. Epub 2008 Jan 26. Eur J Pharmacol. 2008. PMID: 18275955
-
Nicotine behavioral pharmacology: clues from planarians.Drug Alcohol Depend. 2011 Nov 1;118(2-3):274-9. doi: 10.1016/j.drugalcdep.2011.04.001. Epub 2011 May 6. Drug Alcohol Depend. 2011. PMID: 21530106 Free PMC article.
-
Determining the safety of the tobacco cembranoid (1S,2E,4R,6R,7E,11E)-Cembratriene-4,6-diol (4R): A translational study in nonhuman primates.Toxicol Appl Pharmacol. 2024 Jan;482:116772. doi: 10.1016/j.taap.2023.116772. Epub 2023 Nov 28. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol. 2024. PMID: 38036230 Free PMC article.
-
Chemical structures, biosynthesis, bioactivities, and utilisation values for the diterpenes produced in tobacco trichomes.Phytochemistry. 2024 Jul;223:114117. doi: 10.1016/j.phytochem.2024.114117. Epub 2024 May 1. Phytochemistry. 2024. PMID: 38697243
Cited by
-
Clues from planarians about interleukin-17A and stress that result from light avoidance: IL-17A antagonists reduce defensive responding in flatworms.Cytokine. 2023 Oct;170:156345. doi: 10.1016/j.cyto.2023.156345. Epub 2023 Aug 23. Cytokine. 2023. PMID: 37625214 Free PMC article.
-
Kratom pharmacology: Clues from planarians exposed to mitragynine.Physiol Behav. 2021 Oct 1;239:113499. doi: 10.1016/j.physbeh.2021.113499. Epub 2021 Jun 17. Physiol Behav. 2021. PMID: 34146575 Free PMC article.
-
Sucrose produces withdrawal and dopamine-sensitive reinforcing effects in planarians.Physiol Behav. 2013 Mar 15;112-113:8-13. doi: 10.1016/j.physbeh.2013.02.002. Epub 2013 Feb 13. Physiol Behav. 2013. PMID: 23415661 Free PMC article.
-
Anti-hyperalgesic and anti-inflammatory effects of 4R-tobacco cembranoid in a mouse model of inflammatory pain.J Inflamm (Lond). 2024 Jan 24;21(1):2. doi: 10.1186/s12950-023-00373-8. J Inflamm (Lond). 2024. PMID: 38267952 Free PMC article.
-
A Review on Bioactivities of Tobacco Cembranoid Diterpenes.Biomolecules. 2019 Jan 16;9(1):30. doi: 10.3390/biom9010030. Biomolecules. 2019. PMID: 30654586 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Best JB, Morita M. Toxicology of planarians. Hydrobiologia. 1991;227:375–383.
-
- Brenner ED, Stevenson DW, Twigg RW. Cycads: evolutionary innovations and the role of plant-derived neurotoxins. Trends Plant Sci. 2003;8:446–452. - PubMed
-
- Buttarelli FR, Pontieri FE, Margotta V, Palladini G. Acetylcholine/dopamine interaction in planaria. Comp Biochem Physiol C. 2000;125:225–231. - PubMed
-
- Buttarelli FR, Pontieri FE, Margotta V, Palladini G. Cannabinoid-induced stimulation of motor activity in planaria through an opioid receptor-mediated mechanism. Prog Neuro-Psychopharmacol Biol Psychiatry. 2002;26:65–68. - PubMed
-
- Cebrià F, Kudome T, Nakazawa M, Mineta K, Ikeo K, Gojobori T, Agata K. The expression of neural-specific genes reveals the structural and molecular complexity of the planarian central nervous system. Mech Dev. 2002;116:199–204. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

