In vivo biotinylation and capture of HIV-1 matrix and integrase proteins
- PMID: 19490971
- PMCID: PMC2691866
- DOI: 10.1016/j.jviromet.2009.03.017
In vivo biotinylation and capture of HIV-1 matrix and integrase proteins
Abstract
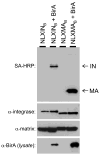
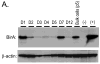
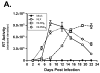
This report describes the adaptation of the biotin ligase BirA-biotin acceptor sequence (BAS) labeling system to biotinylate specific human immunodeficiency virus 1 (HIV-1) proteins in vivo. Two HIV-1 clones were constructed, with the BAS introduced into the matrix region of gag or the integrase region of pol. Specific biotinylation of target proteins in virions was observed when molecular clones were co-expressed with BirA. Both BAS-containing viruses propagated in SupT1 T-cells although replication of the integrase clone was delayed. Further studies demonstrated that the integrase insertion yielded an approximate 40% reduction in single-round infectivity as assessed on MAGI-5 indicator cells, as well as in the in vitro integration activity of preintegration complexes extracted from acutely infected C8166-45 T-cells. Biotinylation of the integrase BAS tag furthermore rendered this virus non-infectious. The matrix viral clone by contrast displayed wild-type behavior under all conditions tested. These results therefore establish a system whereby biotinylated matrix protein in the context of replication-competent virus could be used to label and capture viral protein complexes in vivo.
Figures



References
-
- Belshan M, Mahnke LA, Ratner L. Conserved amino acids of the human immunodeficiency virus type 2 Vpx nuclear localization signal are critical for nuclear targeting of the viral preintegration complex in non-dividing cells. Virology. 2006;346:118–126. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

