Genome-wide screen of promoter methylation identifies novel markers in melanoma
- PMID: 19491193
- PMCID: PMC2720187
- DOI: 10.1101/gr.091447.109
Genome-wide screen of promoter methylation identifies novel markers in melanoma
Abstract
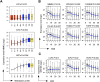
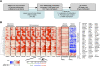
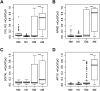
DNA methylation is an important component of epigenetic modifications, which influences the transcriptional machinery aberrant in many human diseases. In this study we present the first genome-wide integrative analysis of promoter methylation and gene expression for the identification of methylation markers in melanoma. Genome-wide promoter methylation and gene expression of eight early-passage human melanoma cell strains were compared with newborn and adult melanocytes. We used linear mixed effect models (LME) in combination with a series of filters based on the localization of promoter methylation relative to the transcription start site, overall promoter CpG content, and differential gene expression to discover DNA methylation markers. This approach identified 76 markers, of which 68 were hyper- and eight hypomethylated (LME, P < 0.05). Promoter methylation and differential gene expression of five markers (COL1A2, NPM2, HSPB6, DDIT4L, MT1G) were validated by sequencing of bisulfite-modified DNA and real-time reverse transcriptase PCR, respectively. Importantly, the incidence of promoter methylation of the validated markers increased moderately in early and significantly in advanced-stage melanomas, using early-passage cell strains and snap-frozen tissues (n = 18 and n = 24, respectively) compared with normal melanocytes and nevi (n = 11 and n = 9, respectively). Our approach allows robust identification of methylation markers that can be applied to other studies involving genome-wide promoter methylation. In conclusion, this study represents the first unbiased systematic effort to determine methylation markers in melanoma and revealed several novel genes regulated by promoter methylation that were not described in cancer cells before.
Figures


References
-
- Bird AP, Wolffe AP. Methylation-induced repression—belts, braces, and chromatin. Cell. 1999;99:451–454. - PubMed
-
- Catalina P, Montes R, Ligero G, Sanchez L, de la Cueva T, Bueno C, Leone PE, Menendez P. Human ESCs predisposition to karyotypic instability: Is a matter of culture adaptation or differential vulnerability among hESC lines due to inherent properties? Mol Cancer. 2008;7:76. doi: 10.1186/1476-4598-7-76. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Cheng E, Trombetta SE, Kovacs D, Beech RD, Ariyan S, Reyes-Mugica M, McNiff JM, Narayan D, Kluger HM, Picardo M, et al. Rab33A: Characterization, expression, and suppression by epigenetic modification. J Invest Dermatol. 2006;126:2257–2271. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous
