Regeneration of the pancreas in adult zebrafish
- PMID: 19491207
- PMCID: PMC2712797
- DOI: 10.2337/db08-0628
Regeneration of the pancreas in adult zebrafish
Abstract
Objective: Regenerating organs in diverse biological systems have provided clues to processes that can be harnessed to repair damaged tissue. Adult mammalian beta-cells have a limited capacity to regenerate, resulting in diabetes and lifelong reliance on insulin. Zebrafish have been used as a model for the regeneration of many organs. We demonstrate the regeneration of adult zebrafish pancreatic beta-cells. This nonmammalian model can be used to define pathways for islet-cell regeneration in humans.
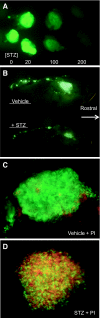
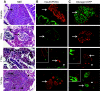
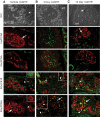
Research design and methods: Adult transgenic zebrafish were injected with a single high dose of streptozotocin or metronidazole and anesthetized at 3, 7, or 14 days or pancreatectomized. Blood glucose measurements were determined and gut sections were analyzed using specific endocrine, exocrine, and duct cell markers as well as markers for dividing cells.
Results: Zebrafish recovered rapidly without the need for insulin injections, and normoglycemia was attained within 2 weeks. Although few proliferating cells were present in vehicles, ablation caused islet destruction and a striking increase of proliferating cells, some of which were Pdx1 positive. Dividing cells were primarily associated with affected islets and ducts but, with the exception of surgical partial pancreatectomy, were not extensively beta-cells.
Conclusions: The ability of the zebrafish to regenerate a functional pancreas using chemical, genetic, and surgical approaches enabled us to identify patterns of cell proliferation in islets and ducts. Further study of the origin and contribution of proliferating cells in reestablishing islet function could provide strategies for treating human diseases.
Figures
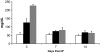
Similar articles
-
Imaging beta cell regeneration and interactions with islet vasculature in transparent adult zebrafish.Zebrafish. 2013 Jun;10(2):249-57. doi: 10.1089/zeb.2012.0813. Epub 2013 May 19. Zebrafish. 2013. PMID: 23682836 Free PMC article.
-
Zebrafish as a model for studying functional pancreatic β cells development and regeneration.Dev Growth Differ. 2018 Aug;60(6):393-399. doi: 10.1111/dgd.12565. Dev Growth Differ. 2018. PMID: 30133710 Review.
-
Impaired pancreatic duct-cell growth in focal areas of regeneration after partial pancreatectomy in the adult Goto-Kakizaki rat, a spontaneous model of non-insulin dependent diabetes mellitus.Histochem J. 2001 Mar;33(3):141-7. doi: 10.1023/a:1017935808074. Histochem J. 2001. PMID: 11508337
-
Progenitor potential of nkx6.1-expressing cells throughout zebrafish life and during beta cell regeneration.BMC Biol. 2015 Sep 2;13:70. doi: 10.1186/s12915-015-0179-4. BMC Biol. 2015. PMID: 26329351 Free PMC article.
-
Zebrafish Pancreas Development and Regeneration: Fishing for Diabetes Therapies.Curr Top Dev Biol. 2017;124:235-276. doi: 10.1016/bs.ctdb.2016.10.005. Epub 2016 Dec 21. Curr Top Dev Biol. 2017. PMID: 28335861 Review.
Cited by
-
The zebrafish as a model for complex tissue regeneration.Trends Genet. 2013 Nov;29(11):611-20. doi: 10.1016/j.tig.2013.07.003. Epub 2013 Aug 6. Trends Genet. 2013. PMID: 23927865 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The Effects of Persimmon (Diospyros kaki L.f.) Oligosaccharides on Features of the Metabolic Syndrome in Zebrafish.Nutrients. 2022 Aug 9;14(16):3249. doi: 10.3390/nu14163249. Nutrients. 2022. PMID: 36014755 Free PMC article.
-
Type I Diabetes in Zebrafish Reduces Sperm Quality and Increases Insulin and Glucose Transporter Transcripts.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Apr 11;24(8):7035. doi: 10.3390/ijms24087035. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 37108202 Free PMC article.
-
Zebrafish for Personalized Regenerative Medicine; A More Predictive Humanized Model of Endocrine Disease.Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2020 Jul 17;11:396. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2020.00396. eCollection 2020. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2020. PMID: 32765420 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Centroacinar Cells Are Progenitors That Contribute to Endocrine Pancreas Regeneration.Diabetes. 2015 Oct;64(10):3499-509. doi: 10.2337/db15-0153. Epub 2015 Jul 7. Diabetes. 2015. PMID: 26153247 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Donath MY, Storling J, Maedler K, Mandrup-Poulsen T: Inflammatory mediators and islet beta-cell failure: a link between type 1 and type 2 diabetes. J Mol Med 2003; 81: 455– 470 - PubMed
-
- Akimenko MA, Mari-Beffa M, Becerra J, Geraudie J: Old questions, new tools, and some answers to the mystery of fin regeneration. Dev Dyn 2003; 226: 190– 201 - PubMed
-
- Chen S, Li C, Yuan G, Xie F: Anatomical and histological observation on the pancreas in adult zebrafish. Pancreas 2007; 34: 120– 125 - PubMed
-
- Ward AB, Warga RM, Prince VE: Origin of the zebrafish endocrine and exocrine pancreas. Dev Dyn 2007; 236: 1558– 1569 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

