The diverse functional roles and regulation of neuronal gap junctions in the retina
- PMID: 19491906
- PMCID: PMC3381350
- DOI: 10.1038/nrn2636
The diverse functional roles and regulation of neuronal gap junctions in the retina
Abstract
Electrical synaptic transmission through gap junctions underlies direct and rapid neuronal communication in the CNS. The diversity of functional roles that electrical synapses have is perhaps best exemplified in the vertebrate retina, in which gap junctions are formed by each of the five major neuron types. These junctions are dynamically regulated by ambient illumination and by circadian rhythms acting through light-activated neuromodulators such as dopamine and nitric oxide, which in turn activate intracellular signalling pathways in the retina.The networks formed by electrically coupled neurons are plastic and reconfigurable, and those in the retina are positioned to play key and diverse parts in the transmission and processing of visual information at every retinal level.
Figures
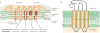




References
-
- Furshpan EJ, Potter DD. Mechanism of nerve-impulse transmission at a crayfish synapse. Nature. 1957;180:342–343. - PubMed
-
- Watanabe A. The interaction of electrical activity among neurons of lobster cardiac ganglion. Jpn J Physiol. 1958;433:283–305. - PubMed
-
- Bennett MVL. In: Cellular Biology of Neurons, Handbook of Physiology, The Nervous System. Kandel ER, editor. Williams & Wilkins; Baltimore: 1977. pp. 357–416.
-
- Söhl G, Maxeiner S, Willecke K. Expression and functions of neuronal gap junctions. Nature Rev Neurosci. 2005;6:191–200. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

