Improvement of in situ PCR by optimization of PCR cycle number and proteinase k concentration: localization of x chromosome-linked phosphoglycerate kinase-1 gene in mouse reproductive organs
- PMID: 19492023
- PMCID: PMC2685019
- DOI: 10.1267/ahc.09011
Improvement of in situ PCR by optimization of PCR cycle number and proteinase k concentration: localization of x chromosome-linked phosphoglycerate kinase-1 gene in mouse reproductive organs
Abstract
In situ polymerase chain reaction (in situ PCR), which can detect a few copies of genes within a cell by amplifying the target gene, was developed to better understand the biological functions of tissues. In this study, we optimized the protocol conditions for the detection of X chromosome-linked phosphoglycerate kinase-1 (pgk-1) gene in paraffin-embedded sections of mouse reproductive organs. The effects of various concentrations of proteinase K (PK) and PCR cycle numbers were examined. To label the amplified DNA, we used digoxigenin-dUTP (Dig), Cy-3-dUTP (Cy-3), or FluorX-dCTP (FluorX). The optimal concentration of PK was 50 microg/ml for the ovary and 10 microg/ml for the testis. Ten PCR cycles were optimal for Dig and 25 cycles were optimal for FluorX and Cy-3 in the ovary and testis. The signal-to-noise ratio of FluorX and Cy-3 for ovarian tissue was better than that of Dig. Using the above conditions, we detected 1-4 and 1-2 spots of pgk-1 in the nuclei of granulosa and germ cells, respectively. Our results indicate that in situ PCR is useful for detecting a specific gene in paraffin-embedded sections under optimized conditions of both PCR cycle number and PK concentration.
Keywords: in situ PCR; ovary; pgk-1; proteinase K; testis.
Figures

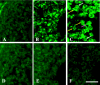
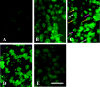

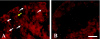
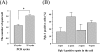
Similar articles
-
Optimized in situ PCR method for the detection of gene transfer vector in histological sections.J Gene Med. 2001 Mar-Apr;3(2):173-8. doi: 10.1002/jgm.163. J Gene Med. 2001. PMID: 11318116
-
In situ PCR for in vivo detection of foreign genes transferred into rat brain.Brain Res. 1998 Feb 9;783(2):347-54. doi: 10.1016/s0006-8993(97)00943-8. Brain Res. 1998. PMID: 9507188
-
Detection of Y-bearing porcine spermatozoa by in situ hybridization using digoxigenin-labeled, porcine male-specific DNA probe produced by polymerase chain reaction.Mol Reprod Dev. 1995 Apr;40(4):455-9. doi: 10.1002/mrd.1080400409. Mol Reprod Dev. 1995. PMID: 7598911
-
Analysis of clonality in human endometriotic cysts based on evaluation of X chromosome inactivation in archival formalin-fixed, paraffin-embedded tissue.Lab Invest. 1998 Feb;78(2):213-8. Lab Invest. 1998. PMID: 9484719 Review.
-
Detection of mRNAs encoding peroxisomal proteins by non-radioactive in situ hybridization with digoxigenin-labelled cRNAs.Histochem Cell Biol. 1997 Oct-Nov;108(4-5):371-9. doi: 10.1007/s004180050178. Histochem Cell Biol. 1997. PMID: 9387930 Review.
Cited by
-
Localisation of abundant and organ-specific genes expressed in Rosa hybrida leaves and flower buds by direct in situ RT-PCR.ScientificWorldJournal. 2012;2012:609597. doi: 10.1100/2012/609597. Epub 2012 May 1. ScientificWorldJournal. 2012. PMID: 22629162 Free PMC article.
-
Detecting the colonization of ericoid mycorrhizal fungi in Vaccinium uliginosum using in situ polymerase chain reaction and green fluorescent protein.Plant Methods. 2020 Jul 30;16:102. doi: 10.1186/s13007-020-00645-x. eCollection 2020. Plant Methods. 2020. PMID: 32760433 Free PMC article.
-
Immunohistochemical Analysis of Histone H3 Modifications in Germ Cells during Mouse Spermatogenesis.Acta Histochem Cytochem. 2011 Aug 27;44(4):183-90. doi: 10.1267/ahc.11027. Epub 2011 Jul 20. Acta Histochem Cytochem. 2011. PMID: 21927517 Free PMC article.
-
Animal models of middle ear cholesteatoma.J Biomed Biotechnol. 2011;2011:394241. doi: 10.1155/2011/394241. Epub 2011 Apr 6. J Biomed Biotechnol. 2011. PMID: 21541229 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Human papillomavirus infection and its possible correlation with p63 expression in cervical cancer in Japan, Mongolia, and Myanmar.Acta Histochem Cytochem. 2009 Dec 29;42(6):181-90. doi: 10.1267/ahc.09030. Epub 2009 Dec 22. Acta Histochem Cytochem. 2009. PMID: 20126571 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Asan E. Progress in focus: recent advances in histochemistry and cell biology. Histochem. Cell Biol. 2002;118:507–525. - PubMed
-
- Bagasra O., Patel D., Bobroski L., Abbasi J. A., Bagasra A. U., Baidouri H., Harris T., El-Roeiy A., Lengvarszky Z., Farzadegan H., Wood C. Localization of human herpesvirus type 8 in human sperms by in situ PCR. J. Mol. Histol. 2005;36:401–412. - PubMed
-
- Catzavelos C., Ruedy C., Stewart A. K., Dube I. A novel method for the direct quantification of gene transfer into cells using PCR in situ. Gene Therapy. 1998;5:755–760. - PubMed
-
- Chen P. C., Pan C., Yang A., Wang L., Chiang H. Detection of Epstein-Bar virus genome within thymic epithelial tumours in Taiwanese patients by nested PCR, PCR in situ hybridization, and RNA in situ hybridization. J. Pathol. 2002;197:684–688. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

