Tolerance to the neuron-specific paraneoplastic HuD antigen
- PMID: 19492067
- PMCID: PMC2688029
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0005739
Tolerance to the neuron-specific paraneoplastic HuD antigen
Abstract
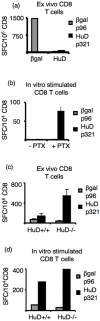
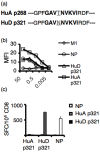
Experiments dating back to the 1940's have led to the hypothesis that the brain is an immunologically privileged site, shielding its antigens from immune recognition. The paraneoplastic Hu syndrome provides a powerful paradigm for addressing this hypothesis; it is believed to develop because small cell lung cancers (SCLC) express the neuron-specific Hu protein. This leads to an Hu-specific tumor immune response that can develop into an autoimmune attack against neurons, presumably when immune privilege in the brain is breached. Interestingly, all SCLC express the onconeural HuD antigen, and clinically useful tumor immune responses can be detected in up to 20% of patients, yet the paraneoplastic neurologic syndrome is extremely rare. We found that HuD-specific CD8+ T cells are normally present in the mouse T cell repertoire, but are not expanded upon immunization, although they can be detected after in vitro expansion. In contrast, HuD-specific T cells could be directly activated in HuD null mice, without the need for in vitro expansion. Taken together, these results demonstrate robust tolerance to the neuronal HuD antigen in vivo, and suggest a re-evaluation of the current concept of immune privilege in the brain.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures


Similar articles
-
Patients with lung cancer and paraneoplastic Hu syndrome harbor HuD-specific type 2 CD8+ T cells.J Clin Invest. 2009 Jul;119(7):2042-51. doi: 10.1172/JCI36131. Epub 2009 Jun 8. J Clin Invest. 2009. PMID: 19509467 Free PMC article.
-
Cell-mediated autoimmunity in paraneoplastic neurological syndromes with anti-Hu antibodies.Ann Neurol. 1999 Feb;45(2):162-7. doi: 10.1002/1531-8249(199902)45:2<162::aid-ana5>3.0.co;2-r. Ann Neurol. 1999. PMID: 9989617
-
No evidence for circulating HuD-specific CD8+ T cells in patients with paraneoplastic neurological syndromes and Hu antibodies.Cancer Immunol Immunother. 2007 Sep;56(9):1501-6. doi: 10.1007/s00262-007-0295-2. Epub 2007 Feb 14. Cancer Immunol Immunother. 2007. PMID: 17597332 Free PMC article.
-
Selection of recombinant anti-HuD Fab fragments from a phage display antibody library of a lung cancer patient with paraneoplastic encephalomyelitis.J Neuroimmunol. 1998 Mar 1;82(2):200-9. doi: 10.1016/s0165-5728(97)00199-9. J Neuroimmunol. 1998. PMID: 9585817
-
DNA vaccination with HuD inhibits growth of a neuroblastoma in mice.Clin Cancer Res. 1998 Nov;4(11):2819-24. Clin Cancer Res. 1998. PMID: 9829748
Cited by
-
Clinical features and outcomes of Chinese patients with anti-γ-aminobutyric acid B receptor encephalitis.Exp Ther Med. 2020 Jul;20(1):617-622. doi: 10.3892/etm.2020.8684. Epub 2020 Apr 23. Exp Ther Med. 2020. PMID: 32509023 Free PMC article.
-
Immunologic privilege in the central nervous system and the blood-brain barrier.J Cereb Blood Flow Metab. 2013 Jan;33(1):13-21. doi: 10.1038/jcbfm.2012.153. Epub 2012 Oct 17. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab. 2013. PMID: 23072749 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Three sensitive assays do not provide evidence for circulating HuD-specific T cells in the blood of patients with paraneoplastic neurological syndromes with anti-Hu antibodies.Neuro Oncol. 2012 Jul;14(7):841-8. doi: 10.1093/neuonc/nos118. Epub 2012 May 15. Neuro Oncol. 2012. PMID: 22591661 Free PMC article.
-
Autoantibodies to Synaptic Receptors and Neuronal Cell Surface Proteins in Autoimmune Diseases of the Central Nervous System.Physiol Rev. 2017 Apr;97(2):839-887. doi: 10.1152/physrev.00010.2016. Physiol Rev. 2017. PMID: 28298428 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Assessment of neuronal autoantibodies in patients with small cell lung cancer treated with chemotherapy with or without ipilimumab.Oncoimmunology. 2017 Nov 27;7(2):e1395125. doi: 10.1080/2162402X.2017.1395125. eCollection 2018. Oncoimmunology. 2017. PMID: 29308329 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials

