Receptor crosstalk: reprogramming B cell receptor signalling to an alternate pathway results in expression and secretion of the autoimmunity-associated cytokine, osteopontin
- PMID: 19493057
- PMCID: PMC2774770
- DOI: 10.1111/j.1365-2796.2009.02103.x
Receptor crosstalk: reprogramming B cell receptor signalling to an alternate pathway results in expression and secretion of the autoimmunity-associated cytokine, osteopontin
Abstract
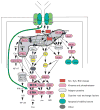
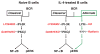
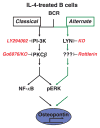
Receptor crosstalk: reprogramming B cell receptor signalling to an alternate pathway results in expression and secretion of the autoimmunity-associated cytokine, osteopontin (Review). J Intern Med 2009; 265: 632-643.Intracellular signalling emanating from the B-cell antigen receptor is considered to follow a discrete course that requires participation by a set of mediators, grouped together as the signalosome, in order for downstream events to occur. Recent work indicates that this paradigm is true only for naïve B cells. Following engagement of the IL-4 receptor, a new, alternate pathway for B-cell receptor (BCR)-triggered intracellular signalling is established that bypasses the need for signalosome elements and operates in parallel with the classical, signalosome-dependent pathway. Reliance on Lyn and sensitivity to rottlerin by the former, but not the latter, distinguishes these two pathways. The advent of alternate pathway signalling leads to production and secretion by B cells of osteopontin (Opn). As Opn is a polyclonal B-cell activator that is strongly associated with a number of autoimmune diseases including lupus and rheumatoid arthritis, this novel finding is likely to be clinically relevant. Our results highlight the potential role of B-cell-derived Opn in immunity and autoimmunity and suggest that stress-related IL-4 expression might act to strengthen immunoglobulin secretion at the risk of autoantibody formation. Further, these results illustrate receptor crosstalk in the form of reprogramming, whereby engagement of one receptor (IL-4R) produces an effect that persists after the original ligand (IL-4) is removed and results in alteration of the pathway, and outcome, of signalling via a second receptor (BCR) following its activation.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have nothing to declare.
Figures
Similar articles
-
B cell receptor crosstalk: B cells express osteopontin through the combined action of the alternate and classical BCR signaling pathways.Mol Immunol. 2009 Feb;46(4):587-91. doi: 10.1016/j.molimm.2008.07.029. Epub 2008 Oct 25. Mol Immunol. 2009. PMID: 18952291 Free PMC article.
-
The Alternate Pathway for BCR Signaling Induced by IL-4 Requires Lyn Tyrosine Kinase.J Mol Biol. 2021 Jan 8;433(1):166667. doi: 10.1016/j.jmb.2020.10.002. Epub 2020 Oct 13. J Mol Biol. 2021. PMID: 33058880 Review.
-
Cutting Edge: B cell receptor (BCR) cross-talk: the IL-4-induced alternate pathway for BCR signaling operates in parallel with the classical pathway, is sensitive to Rottlerin, and depends on Lyn.J Immunol. 2007 Apr 15;178(8):4726-30. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.178.8.4726. J Immunol. 2007. PMID: 17404251
-
Signal Integration by Translocation and Phosphorylation of PKCδ in the B Cell Alternate Pathway.J Immunol. 2021 Nov 1;207(9):2288-2296. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.2100295. Epub 2021 Sep 29. J Immunol. 2021. PMID: 34588218 Free PMC article.
-
Altered B cell signalling in autoimmunity.Nat Rev Immunol. 2017 Jul;17(7):421-436. doi: 10.1038/nri.2017.24. Epub 2017 Apr 10. Nat Rev Immunol. 2017. PMID: 28393923 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Introduction: The first Merinoff Symposium, 'Systemic Lupus: Bringing Science to the Patient'.J Intern Med. 2009 Jun;265(6):622-4. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2796.2009.02097.x. J Intern Med. 2009. PMID: 19493055 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
Norepinephrine triggers an immediate-early regulatory network response in primary human white adipocytes.BMC Genomics. 2018 Nov 3;19(1):794. doi: 10.1186/s12864-018-5173-0. BMC Genomics. 2018. PMID: 30390616 Free PMC article.
-
Osteopontin and malaria: no direct effect on parasite growth, but correlation with P. falciparum-specific B cells and BAFF in a malaria endemic area.BMC Microbiol. 2021 Nov 6;21(1):307. doi: 10.1186/s12866-021-02368-y. BMC Microbiol. 2021. PMID: 34742229 Free PMC article.
-
A novel Lyn-protein kinase Cδ/ε-protein kinase D axis is activated in B cells by signalosome-independent alternate pathway BCR signaling.Eur J Immunol. 2013 Jun;43(6):1643-50. doi: 10.1002/eji.201242830. Epub 2013 Apr 12. Eur J Immunol. 2013. PMID: 23457006 Free PMC article.
-
Stress-Induced Epstein-Barr Virus Reactivation.Biomolecules. 2021 Sep 18;11(9):1380. doi: 10.3390/biom11091380. Biomolecules. 2021. PMID: 34572593 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Chambers SA, Isenberg D. Anti-B cell therapy (rituximab) in the treatment of autoimmune diseases. Lupus. 2005;14:210–4. - PubMed
-
- Goldblatt F, Isenberg DA. Anti-CD20 monoclonal antibody in rheumatoid arthritis and systemic lupus erythematosus. Handb Exp Pharmacol. 2008;181:163–81. - PubMed
-
- Tieng AT, Peeva E. B-cell-directed therapies in systemic lupus erythematosus. Semin Arthritis Rheum. 2008;38:218–27. - PubMed
-
- Mease PJ. B cell-targeted therapy in autoimmune disease: rationale, mechanisms, and clinical application. J Rheumatol. 2008;35:1245–55. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

