Antigenic protein modifications in Ehrlichia
- PMID: 19493209
- PMCID: PMC2731653
- DOI: 10.1111/j.1365-3024.2009.01099.x
Antigenic protein modifications in Ehrlichia
Abstract
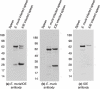
To develop effective vaccination strategies against Ehrlichia, we have previously reported developing an animal model of cross-protection in which C57BL/6 mice primed with E. muris were resistant to lethal infection with Ixodes ovatus ehrlichia (IOE). Polyclonal antibody produced in mice after priming with E. muris and later injected with IOE-detected antigenic proteins in E. muris and IOE cell lysates. Cross-reaction of antigenic proteins was observed when we probed both the E. muris and IOE cell lysates with IOE and E. muris-specific polyclonal antibody. Analysis of the total proteins of E. muris and IOE by two dimensional electrophoresis showed that both E. muris and IOE have the same antigenic proteins. Finally, studies on post-translational protein modifications using a novel technique, Eastern blotting, showed that E. muris proteins are more lipoylated and glycosylated than those of IOE.
Figures



Similar articles
-
NK Cell-Mediated Regulation of Protective Memory Responses against Intracellular Ehrlichial Pathogens.PLoS One. 2016 Apr 19;11(4):e0153223. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0153223. eCollection 2016. PLoS One. 2016. PMID: 27092553 Free PMC article.
-
Protective heterologous immunity against fatal ehrlichiosis and lack of protection following homologous challenge.Infect Immun. 2008 May;76(5):1920-30. doi: 10.1128/IAI.01293-07. Epub 2008 Feb 19. Infect Immun. 2008. PMID: 18285501 Free PMC article.
-
T-Cell-independent humoral immunity is sufficient for protection against fatal intracellular ehrlichia infection.Infect Immun. 2007 Oct;75(10):4933-41. doi: 10.1128/IAI.00705-07. Epub 2007 Jul 30. Infect Immun. 2007. PMID: 17664264 Free PMC article.
-
Persistent infection contributes to heterologous protective immunity against fatal ehrlichiosis.Infect Immun. 2009 Dec;77(12):5682-9. doi: 10.1128/IAI.00720-09. Epub 2009 Oct 5. Infect Immun. 2009. PMID: 19805532 Free PMC article.
-
Overproduction of TNF-alpha by CD8+ type 1 cells and down-regulation of IFN-gamma production by CD4+ Th1 cells contribute to toxic shock-like syndrome in an animal model of fatal monocytotropic ehrlichiosis.J Immunol. 2004 Feb 1;172(3):1786-800. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.172.3.1786. J Immunol. 2004. PMID: 14734762
Cited by
-
Immunization with Ehrlichia P28 outer membrane proteins confers protection in a mouse model of ehrlichiosis.Clin Vaccine Immunol. 2011 Dec;18(12):2018-25. doi: 10.1128/CVI.05292-11. Epub 2011 Oct 26. Clin Vaccine Immunol. 2011. PMID: 22030371 Free PMC article.
-
Structure-based vaccines provide protection in a mouse model of ehrlichiosis.PLoS One. 2011;6(11):e27981. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0027981. Epub 2011 Nov 17. PLoS One. 2011. PMID: 22114733 Free PMC article.
-
Proteomic analysis of the Ehrlichia chaffeensis phagosome in cultured DH82 cells.PLoS One. 2014 Feb 18;9(2):e88461. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0088461. eCollection 2014. PLoS One. 2014. PMID: 24558391 Free PMC article.
-
Exit mechanisms of the intracellular bacterium Ehrlichia.PLoS One. 2010 Dec 20;5(12):e15775. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0015775. PLoS One. 2010. PMID: 21187937 Free PMC article.
-
GroEL is an immunodominant surface-exposed antigen of Rickettsia typhi.PLoS One. 2021 Jun 10;16(6):e0253084. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0253084. eCollection 2021. PLoS One. 2021. PMID: 34111210 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Walker DH. Ehrlichia under our noses and no one notices. Arch Virol Suppl. 2005;19:147–156. - PubMed
-
- Ismail N, Soong L, McBride JW, et al. Overproduction of TNF-α by CD8+ type 1 cells and down-regulation of IFN-γ production by CD4+ Th1 cells contribute to toxic shock–like syndrome in an animal model of fatal monocytotropic ehrlichiosis. J Immunol. 2004;172:1786–1800. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

