Antigenic protein modifications in Ehrlichia
- PMID: 19493209
- PMCID: PMC2731653
- DOI: 10.1111/j.1365-3024.2009.01099.x
Antigenic protein modifications in Ehrlichia
Abstract
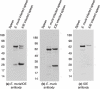
To develop effective vaccination strategies against Ehrlichia, we have previously reported developing an animal model of cross-protection in which C57BL/6 mice primed with E. muris were resistant to lethal infection with Ixodes ovatus ehrlichia (IOE). Polyclonal antibody produced in mice after priming with E. muris and later injected with IOE-detected antigenic proteins in E. muris and IOE cell lysates. Cross-reaction of antigenic proteins was observed when we probed both the E. muris and IOE cell lysates with IOE and E. muris-specific polyclonal antibody. Analysis of the total proteins of E. muris and IOE by two dimensional electrophoresis showed that both E. muris and IOE have the same antigenic proteins. Finally, studies on post-translational protein modifications using a novel technique, Eastern blotting, showed that E. muris proteins are more lipoylated and glycosylated than those of IOE.
Figures

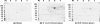


References
-
- Walker DH. Ehrlichia under our noses and no one notices. Arch Virol Suppl. 2005;19:147–156. - PubMed
-
- Ismail N, Soong L, McBride JW, et al. Overproduction of TNF-α by CD8+ type 1 cells and down-regulation of IFN-γ production by CD4+ Th1 cells contribute to toxic shock–like syndrome in an animal model of fatal monocytotropic ehrlichiosis. J Immunol. 2004;172:1786–1800. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

